The air standard cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that, as the name suggests, uses air as a working fluid. These are the ideal cycle on which the actual engines work.
Let’s discuss this in detail, including its assumptions, formulae, and how it differs from the actual cycle.
Contents:
What is Air standard cycle?
The air standard cycle is a thermodynamic power cycle that converts heat energy into mechanical power by considering air as a working fluid with constant specific heats (Cp & Cv).
In this cycle, the air is the only working fluid that goes through changes in its thermodynamic properties to convert heat into mechanical power.
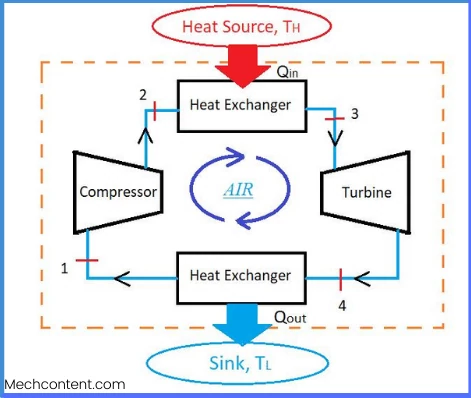
In this cycle, there is no internal energy generation by means of burning any fuel inside the engine.
The heat is externally added by means of a heat exchanger & externally rejected by using a heat exchanger to the sink.
It consists of a non-flow process. It means that a certain amount of air is continuously perform successive cycles. No intake or exhaust of air is permitted into the cycle.
Hence, it works as a closed cycle with no mass transfer. Working fluid air is considered an ideal gas with constant specific heat.
Following are examples of air standard cycle:
- Carnot cycle
- Otto cycle or Petrol cycle
- Diesel cycle
- Air standard dual cycle
- Brayton cycle etc.
Air standard cycle assumptions:
Following are the assumptions:
- Air is considered as working fluid.
- Air has constant specific heat.
- Air behave as ideal gas.
- All processes in cycle as internally reversible.
- For air Change in K.E.= 0, Change in P.E.= 0
- No internal heat generation.
- heat is added & rejected externally.
- The cycle is closed & processes are non-flow processes.
- There is no frictional losses.
Important formulae:
1] Thermal efficiency:
Thermal efficiency for the air standard cycle (also known as air standard efficiency) is given by,
`eta _{th}= frac{W_{Net}}{Q_{s}}`
Where,
WNet = Net work = WTurbine – Wcompressor
Qs = Heat supplied
2] Net work ratio (WRNet):
It is given by,
`WR_{Net}=frac{W_{Net}}{W_{\text{Turbine}}}`
`WR_{Net}` = `frac{W_{\text{Turbine}}-W_{\text{compressor}}}{W_{\text{Turbine}}}`
`WR_{Net}=1-frac{W_{\text{compressor}}}{W_{\text{Turbine}}}`
3] Back work ratio:
It is given by,
`WR_{Back}=frac{W_{\text{compressor}}}{W_{\text{Turbine}}}`
Difference between Air standard cycle and Actual cycle:
Here, we will discuss how Air standard cycle is different from the Actual cycle:
| Sr. No. | Air standard cycle | Actual cycle |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Air is working fluid. | A mixture of air and fuel is a working fluid. |
| 2 | Air behaves as the ideal gas. | Working fluid does not always behave like an ideal gas. |
| 3 | Specific heat of air is constant. | Specific heats are variable with respect to temperature. |
| 4 | Processes are non-flow processes. | Working fluid flows continuously. |
| 5 | No internal heat generation. | Generation of energy by burning of fuel with air. |
| 6 | Heat added externally. | Energy is generated inside the engine. |
| 7 | No frictional losses. | Frictional losses are present. |
| 8 | This cycle is completely closed. | Because of the inlet and exhaust process, the cycle is not closed. |