What is Dual cycle?
Dual cycle is the air standard cycle, which is a combination of the thermodynamic Otto cycle and Diesel cycle.
This thermodynamic power cycle consists of the two constant volume processes, two adiabatic processes, and one isobaric process (Constant pressure).
Contents:
Dual cycle PV and TS diagram:
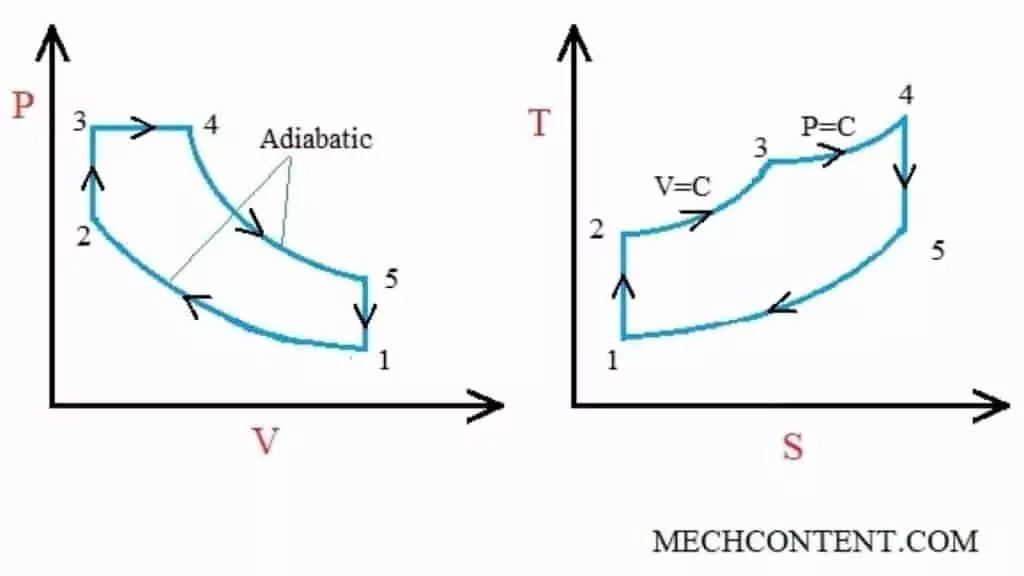
The cycle consists of following processes:
Process 1-2 (Isentropic compression): In this process, the air is compressed in isentropic (reversible adiabatic) manner from state 1 to 2.
Process 2-3 (Constant volume heat addition): During this process, the volume of the air is kept constant and heat is added externally to the air.
Process 3-4 (Constant pressure heat addition): In this process, the heat is added to the air by keeping the pressure constant.
Process 4-5 (Isentropic expansion): The high pressure air is expanded isentropically to obtain work.
Process 5-1 (Constant volume heat rejection): In this process, the heat is rejected by the air in adiabatic manner.
Thermodynamic analysis of cycle:
Let’s analyze each of the process in detail.
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression
For reversible adiabatic process,
Q1-2 = 0
By compression of air from 1 to 2 temperature of air increases from T1 to T2 hence change in internal energy is given by :-
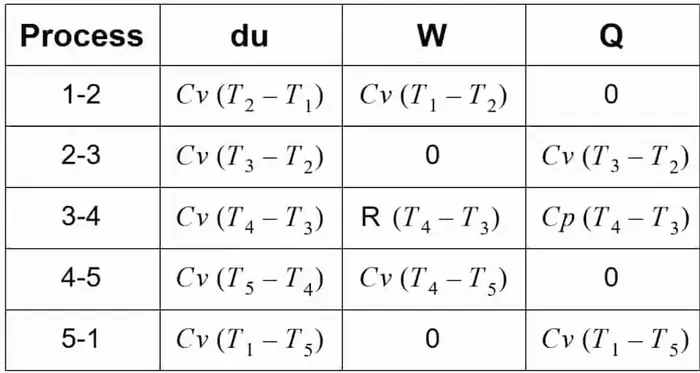
du1-2 = Cv( T2 – T1)
Now by First law of thermodynamics,
Q1-2 = du1-2 +W1-2
0 = Cv( T2 – T1) + W1-2
W1-2= Cv( T1 – T2 )
W1-2 = Cv( T1 – T2 )
Process 2-3: Constant volume heat addition:
For the isochoric process, Change in volume (`delta v=0`)
∴ W2-3 = 0
Here, temperature rises from T2 to T3. Hence, change in internal energy is given by,
du2-3 = Cv( T3-T2 )
Now to find heat transfer (Q), By first law of thermodynamics,
Q2-3 = du2-3 + W2-3
Q2-3 = Cv( T3 – T2 ) + 0
Q2-3 = Cv( T3 – T2 )
Process 3-4: Constant pressure heat addition:
For constant pressure process,
W3-4 = P(V4 – V3)
As PV=RT, the above equation can write in the form of temperature as follows,
W3-4 = R(T4 – T3)
The temperature rises from T3 to T4. Hence internal energy change is given by,
du3-4 = Cv(T4 – T3)
Now to find rate of heat transfer by first law of thermodynamics,
Q3-4 =du3-4 + W3-4
Q3-4 = Cv( T4 – T3) + R(T4 – T3)
Q3-4 = (Cv + R)(T4 – T3)
Q3-4 = (Cv + Cp – Cv)(T4 – T3)
Q3-4 = Cp( T4 – T3)
Process 4-5: Reversible expansion for the reversible adiabatic process:
Q4-5 = 0
By expansion of air from 4 to 5, the temperature of the air decreases from T4 to T5. Hence, the change in internal energy is given by,
du4-5 = Cv(T5 -T4)
Now, by the first law of thermodynamics,
Q4-5 =du4-5 + W4-5
0 = Cv(T5 – T4) + W4-5
W4-5 = Cv(T4 – T5)
Process 5-1: Constant volume heat rejection:
For constant volume process,
W5-1 = 0
In this process temperature of air decreases from T5 to T1. Hence, change in internal energy is given by,
du5-1 = Cv(T1 – T5)
Now by first law of thermodynamics,
Q5-1 =du5-1 + W5-1
Q5-1 = Cv(T1 – T5) + 0
Q5-1 = Cv( T1 – T5)
All parameters are summarized below:
Dual cycle application:
1] Heavy diesel engine.
Read also: