If you are interested to know about four-stroke engines, then this article will help you to understand in an easy way.
Single cylinder 4-stroke engine working can be understood by knowing the process which consists of 4 number of strokes. The engine does two cycles of the crankshaft by completing four strokes of the engine i.e. suction, compression, expansion, and exhaust.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- Introduction:
- How a single cylinder 4-stroke engine works?
- Construction of four stroke engine:
- Types of 4 stroke engine:
4.1. Four stroke petrol engine
4.2. Four stroke diesel engine
4.3. Single cylinder engine
4.4. Multi cylinder engine - Advantages of 4 stroke engine:
- Disadvantages of 4 stroke engine:
- Applications of the 4 stroke engine:
Introduction:
Currently, huge applications in the automobile industry, power generators, water pumps, lawn movers, etc. are working on the principle of four stroke engines.
The term four stroke engine was firstly used by Nikolaus Otto in 1876. He had invented the first four stroke internal combustion engine.
The meaning of some terms used in this article are as follows
- Stroke: It is the travel of the piston from TDC to BDC of the cylinder block.
- T.D.C.: Top dead center is the position of the piston nearest to the cylinder head.
- B.D.C.: Bottom dead center is the position of the piston farthest to the cylinder head.
The name itself says this Internal combustion engine consists of four strokes of the piston to complete one power cycle. Out of the four strokes, one is a power stroke and the remaining three are idle strokes.
The four strokes of the piston are complete within two revolutions of the crankshaft.
How a single cylinder 4-stroke engine works?
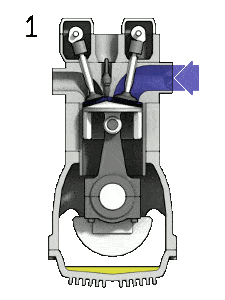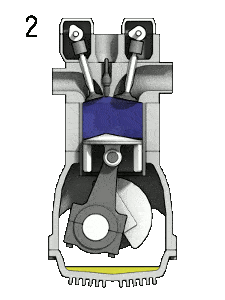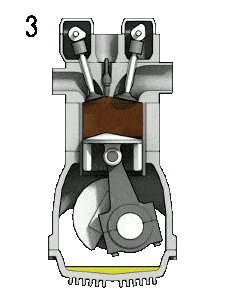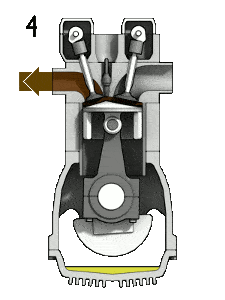
The working of four stroke engine consists of four strokes of piston and two crank revolutions.
- 1st stroke (Suction stroke): In this stroke fresh charge of air or air-fuel mixture is taken inside. For this process piston moves from TDC to BDC.
- 2nd stroke (Compression stroke): The fresh charge is compressed by moving the piston from BDC to TDC.
- 3rd stroke (Expansion Stroke): It is also known as the power stroke. In this stroke compressed charge is combusted which generates high-pressure hot gases inside of a cylinder. It pushes the piston from TDC to BDC In this process hot gases are expanded from TDC to BDC.
- 4th stroke (Exhaust stroke): In the ideal cycle, it is known as the heat rejection process. In this stroke, the hot gases (Combustion products) are expelled out from the cylinder by moving the piston from BDC to TDC.
These all four strokes create one heat engine cycle which gives two complete revolutions of the crankshaft.
Construction of four stroke engine:
The construction of four stroke engine is more complex than two stroke engines. It is consist of the following components:
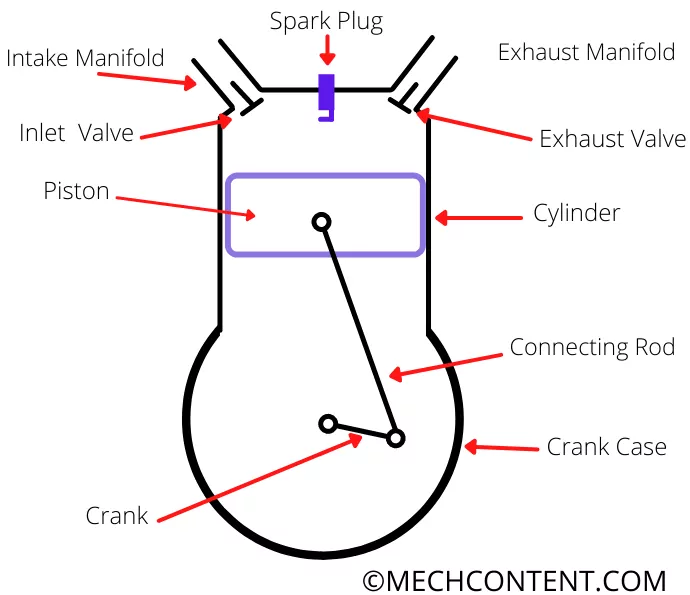
1] Cylinder: A cylinder is generally made up of cast iron. The piston moves inside of the cylinder
2] Cylinder head: The valves and spark plug/fuel injector is mounted onto the cylinder head. The intake and exhaust manifold are connected to the cylinder head.
3] Piston: It is a reciprocating element that reciprocates into the cylinder. The other end of the piston is connected to the connecting rod. It is generally made up of aluminum alloy.
4] Inlet manifold: The fresh charge is supplied to the cylinder from the intake manifold. The main purpose of the intake manifold is to supply the charge equally in multi-cylinder engines.
5) Exhaust manifold: The exhaust gases from the cylinder are expelled out through the exhaust manifold.
6) Inlet valve: The inlet valves are used to control the flow of fresh charge into the cylinder. It opens only at a suction stroke and remains closed in other strokes.
The movement of the inlet valve is controlled by the camshaft.
7) Exhaust valve: the exhaust valve is used to control the flow of burned exhaust gases. It opens only at exhaust stroke and remains closed in others strokes. The movement of the outlet valve is also controlled by the camshaft.
8) Piston rings: Piston rings are used to seal the combustion chambers. It avoids leakage of gases from the combustion chamber to the crankcase. It’s generally of two types compression rings and oil control rings.
9) Spark plug: It is used in petrol engines for the ignition of compressed charge.
10) Fuel injector: It is used in diesel engines to spray fuel into the Compressed air.
11) Connecting rod and crank: The main purpose of connecting rod and crank is to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston to the rotary motion of the crankshaft.
These are all basic details about the construction of four stroke engines.
Types of 4 stroke engine:
As per the working cycle and number of cylinders, the classification of four stroke engine is as follows:
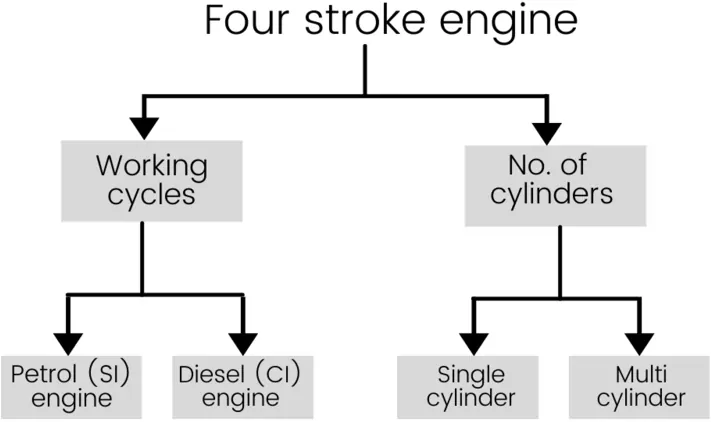
Let’s see all kinds of four stroke engines in brief one by one,
A) Four stroke petrol engine
The petrol engine is also known as a spark ignition (SI) engine. The four stroke petrol engine is based on the Otto cycle invented by Nicholas auto in 1876.
The compression ratio for petrol engines varies from 10 to 13.5.
Otto cycle:
The Otto cycle consists of the following cycles,
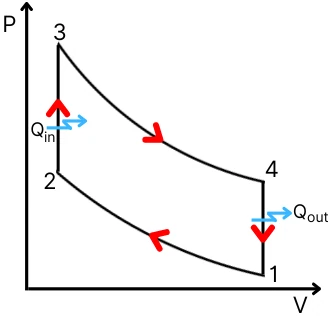
- Process 1-2: Isentropic compression
- Process 2-3: Constant volume heat addition.
- Process 3-4: Isentropic expansion
- Process 4-1: Constant volume heat rejection.
Working:
The working is as follows:-
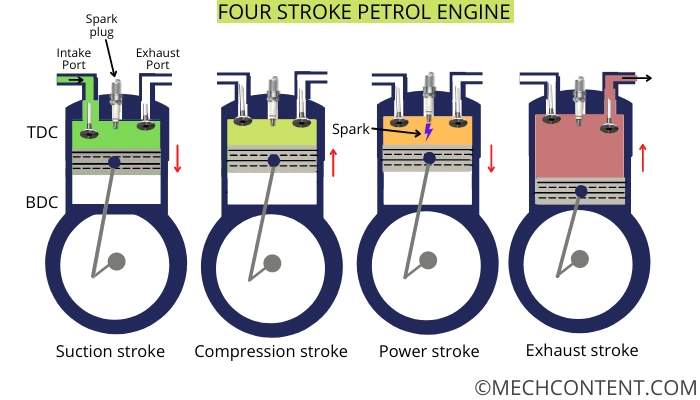
1) The process starts with suction stroke, at the time of suction stroke the inlet valve is open and the exhaust valve is in closed condition. The piston moves from TDC to BDC. Piston sucks the fresh charge from the intake manifold.
2) After the suction of fresh charge both valves get closed. The piston moves from BDC to TDC to compress the fresh charge.
3) After reaching the piston to the top dead centre, the spark plug ignites the charge in the cylinder. The pressure in the cylinder increases and it pushes the piston to the bottom dead centre.
4) Now the exhaust valve gets opened after the piston reaching the BDC the piston starts to move toward TDC to expel out the exhaust gases.
5) This cycle is repeated continuously.
B) Four stroke diesel engine
The diesel engine is also known as the compression ignition engine (CI engine). The four stroke diesel engine is based on the diesel cycle invented by Rudolf diesel auto in 1895.
The compression ratio for diesel engines varies from 14 to 25.
Diesel cycle:
The diesel cycle consists of the following cycles,
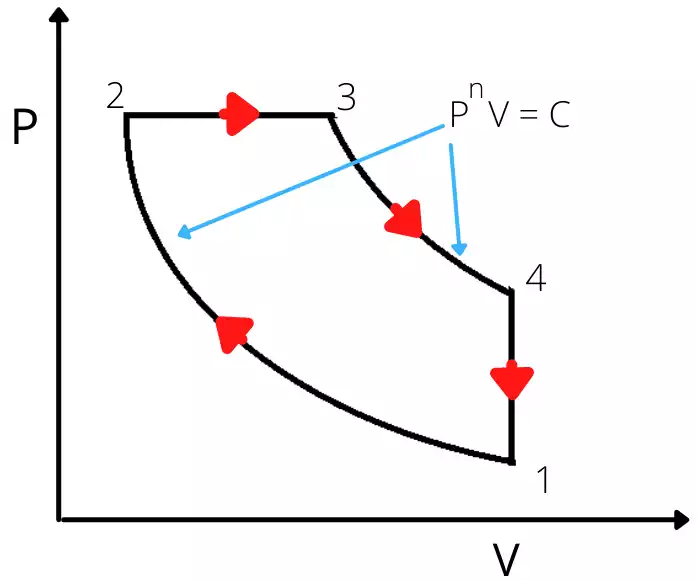
- Process 1-2: Isentropic compression
- Process 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition
- Process 3-4: Isentropic expansion
- Process 4-1: Constant volume heat rejection.
Working:
The working is as follows:-
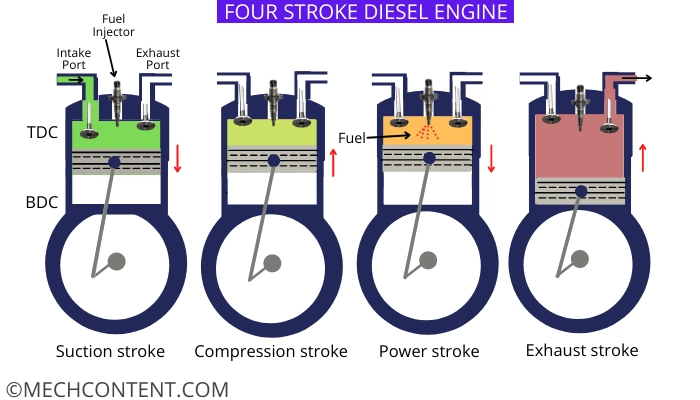
1) The process starts with suction stroke at the time of suction stroke the inlet valve is open and the exhaust valve is in closed condition. The piston moves from TDC to BDC. Piston sucks the fresh air from the intake manifold.
2) After the suction of fresh air both valves get closed. The piston moves from BDC to TDC to compress the fresh air. hence the air gets heated due to the high compression ratio.
3) After reaching the piston to the top dead center, the fuel injector injects fuel into the cylinder. Due to the high temperature of Compressed air the fuel ignited automatically. The pressure in the cylinder increases and it pushes the piston to the bottom dead center.
4) Now the exhaust valve gets opened after the piston reaching at the BDC then piston starts to move toward TDC to expel out the exhaust gases.
5) This cycle is repeated continuously.
C) Single cylinder engine
It means that the engine has a single cylinder only.
The construction of single cylinder engine is simple than the multi-cylinder engine.
The engine can be cooled by surrounding air by providing fins. Hence the weight of the engine is less as compared to water-cooled engines.
But due to the single cylinder, the engine provides only one power stroke in two complete revolutions of the shaft. hence power delivered to the crankshaft is in pulsating form, Which increases vibration in the engine.
To avoid these fluctuations, the engine requires a heavy flywheel.
Generally, single cylinder engines are manufactured as a petrol engine.
Applications:- Motorcycle, auto-rickshaw, lawn movers, etc.
D) Multi cylinder engine
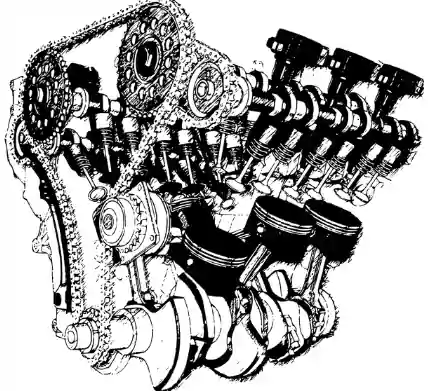
By its name, the multi-cylinder engine has more than one cylinder to rotate a single crankshaft.
The multi-cylinder engines are used to smooth the power fluctuations and vibrations that occur in single cylinder engine.
The number of cylinders used in multi-cylinder engines are up to 10 or 12.
Depending on the arrangement of cylinders, the multi-cylinder engines are classified as follows:
- Inline engine: The cylinders are arranged in a line above the crankshaft.
- V engines: The pistons are inclined in such a way that it looks like the English letter ‘V’.
- Radial engines: In this, the cylinders are aligned radially and the connecting rods are connected to a single crank.
- Delta engines (Δ): The three cylinders are arranged in shape of delta (Δ) and each cylinder contains two pistons in opposite direction. The complete assembly looks like Greek letter delta.
- W engines: In this engine four cylinder are arranged in such was that the connecting rods of all pistons are connected to the common crank.
Advantages of 4 stroke engine:
The advantages of the four-stroke engine are as follows:-
- The engine produces less torque with high RPM.
- Lower smoke generation.
- The lubrication required is very less as compared to two stroke engine, as in the case of two stroke engine lubricant has to be directly mixed with fuel.
- Noise generation is less in this engine.
- Stroke engines are more durable.
- The engine has higher thermal efficiency.
Disadvantages of 4 stroke engine:
- For same amount of power output the engines size is larger.
- Four stroke engine are more complicated than two stroke engines.
- It has more moving parts hence it requires heavy flywheel.
- Stroke engines are expensive.
- Four stroke engines are difficult to cold start.
Applications of the 4 stroke engine:
The four stroke engine has a wide range of applications because of its higher thermal efficiency and higher RPM. It is used in applications where the efficiency requirement is higher.
The applications of 4 stroke petrol engines are:-
- Motorcycles
- Buses
- Trucks
- Auto rickshaw
- Generator sets
- Aeroplane propellers
- Boats
- Air compressors.
FAQs on 4 stroke engine:
-
What are 4 stroke engines used in?
The working of four stroke engine consists of four strokes of piston which are Suction, Compression, Expansion, Exhaust. This all four strokes of the piston completes within two revolutions of the crankshaft.
-
What are the four processes in a four stroke engine?
There are four processes are involved in four stroke engine are Suction, Compression, Expansion, and Exhaust. These all four processes create one heat engine cycle which gives two complete revolutions of the crankshaft.
Media credits:
- Four stroke petrol engine gif By Zephyris – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0