In some circumstances, driving your car with only two wheels is insufficient to provide adequate traction force. Thus in such situations, it is necessary to drive all the wheels.
For this purpose, the transfer case helps to supply power to both front and rear propeller shafts so that the car gets shifted to the 4-wheel-drive mode. So In this article, we are discussing the transfer case in detail.

In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- What is a Transfer case?
- Functions of the transfer case:
- Transfer case diagram and construction:
- How does a transfer case work?
- Types of transfer case:
5.1. Based on the drive used:
5.2. Based on the housing of transfer case: - Transfer case vs Transmission:
- What is transfer case oil?
- Bad transfer case symptoms:
- FAQs:
What is a Transfer case?
Transfer case is the part connected after the transmission box of 4 wheel drive/ All wheel drive vehicle, which transfers the power from the transmission to the front wheels and rear wheels.
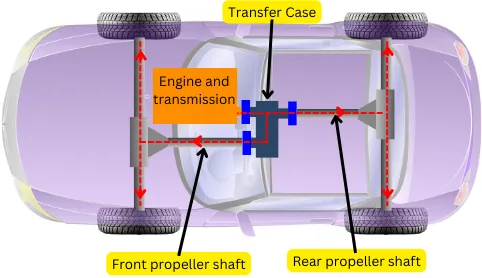
In other words, the transfer case connects the front propeller shaft and the rear propeller shaft to the transmission output shaft. The propeller shafts are further connected to the front and rear differential, which makes it possible to transfer power to all wheels of the automobile.
The transfer case is located after the transmission and it also has a provision for selecting the drive mode (2WD or 4WD).
Some of the transfer cases also use a reduction unit to provide two different speed ratios (High or low).
Thus these transfer case consists of two different sections: Drive section (2WD/4WD) and the reduction section.
These two different sections provide the following different combinations to drive the vehicle:-
2H (2 wheel drive at high speed)
4L (4 wheel drive at low speed)
4H (4 wheel drive at high speed)
Purpose of transfer case:
The various purpose of the transfer case in the vehicle are as follows:
1] Stability on Icy Roads: While driving on the icy road, the 2-wheel drive is not efficient to develop sufficient traction so that the vehicle can skid. Therefore in such conditions, the transfer case powers all wheels of the vehicle, so that it can develop the necessary traction to move a vehicle on road.
2] Grip on Muddy Terrain: Similarly while moving on a muddy road, the transfer case rotates all 4 wheels at a lower speed (high torque).
3] Adaptation for Off-Road Conditions: On off-road or on unpaved roads, the transfer case drives the front wheels and the rear wheels at different speeds.
4] Switching Between 4WD and 2WD: It also helps to convert the drive from 4WD to 2WD to drive the vehicle on a regular road.
Functions of the transfer case:
Following are the important functions of the transfer case:
- Splits power from the transmission to the rear axle and the front axle.
- Provides two different gear ratios.
- The central differential transfer case allows the front wheels and the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds.
Transfer case diagram and construction:
The transfer case consists of the following two main sections:
a] Reduction section: The reduction section in the transfer case provides two different gear ratios (i.e. low and high). For this purpose, the transfer case uses constant mesh gears with a sliding clutch or it uses a planetary gear with a sliding clutch.
By using the sliding mechanism, the user can select the gear ratio of the transfer case.
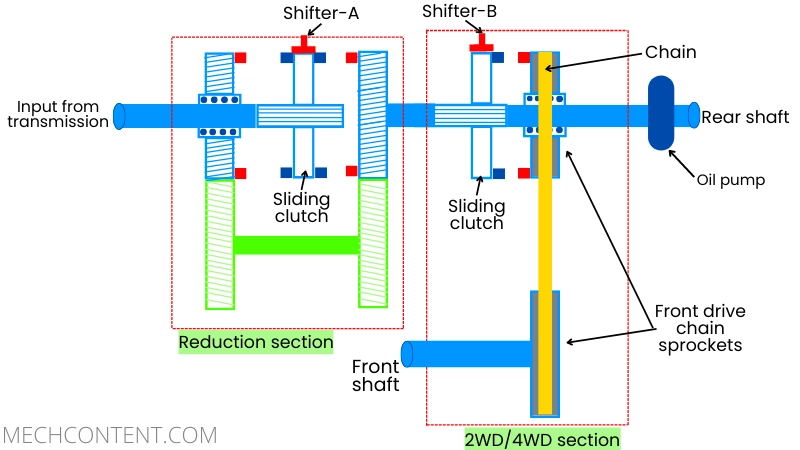
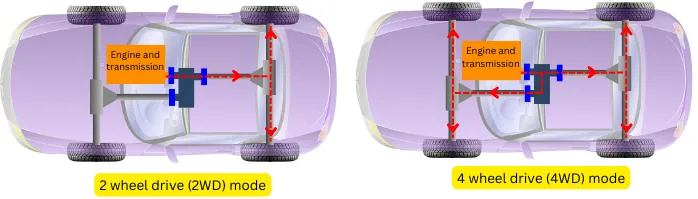
b] 2WD/4WD section: This section of the transfer case helps to choose the 2-wheel drive mode or the 4-wheel drive mode.
In 2-wheel drive mode, the power is transmitted only to the pair of rear wheels while in 4-wheel drive mode, the power is transmitted to the front wheels as well as to the rear wheels.
For this purpose, the transfer case uses a chain drive or gear drive between the rear output shaft and the front output shaft. The sprocket/gear on the rear output shaft is mounted with the help of a bearing.
The engagement between this chain sprocket and the rear output shaft is controlled with the help of a sliding clutch.
Other than these, the transfer case also uses an oil pump that continuously lubricates the planetary gears and bearings.
The front output of the transfer case is connected to the front differential through the front propeller shaft, and the rear output is connected to the rear differential through the rear propeller shaft.
Some individuals may get confused with the transfer case and differential, we have this article that will help you to distinguish between the transfer case and differential unit.
How does a transfer case work?
The transfer case in a vehicle has two different sections which can be controlled by the use of two different shifting mechanisms.
One of the sections is known as the 4WD/2WD section which helps to change the drive mode of a vehicle from 4 wheel drive to two-wheel drive and vice versa.
Another section is known as the reduction section which provides two different speed ratios (High and low).
Depending on the combinations between these two sections, the driver can obtain the following four different drive modes from the transfer case:
A] 2H (2 wheel drive at high-velocity ratio):
In this mode, the transfer case transmits power only to the rear two wheels at a higher speed ratio.
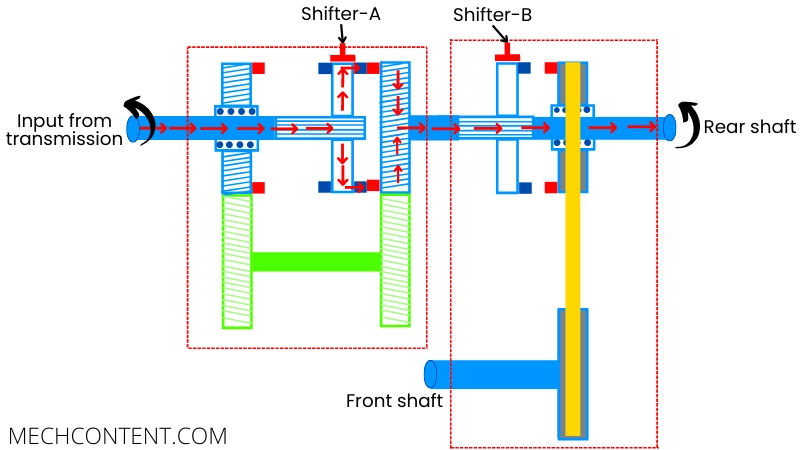
For this purpose, the shifter mechanism-A connects the input shaft to the right side gear with the help of a sliding clutch. Thus the power is transmitted further without speed reduction.
The shifter mechanism-B disconnects the contact between the rear output shaft and the chain drive of the front output shaft.
Thus the power is only transmitted to the rear two wheels at a high-velocity ratio. This mode of the transfer case is suitable for the everyday running of vehicles on the non-slippery road.
B] 4L (4 wheel drive at low-speed ratio):
In this mode, the transfer case transmits power to the front and rear wheels at a lower speed ratio.
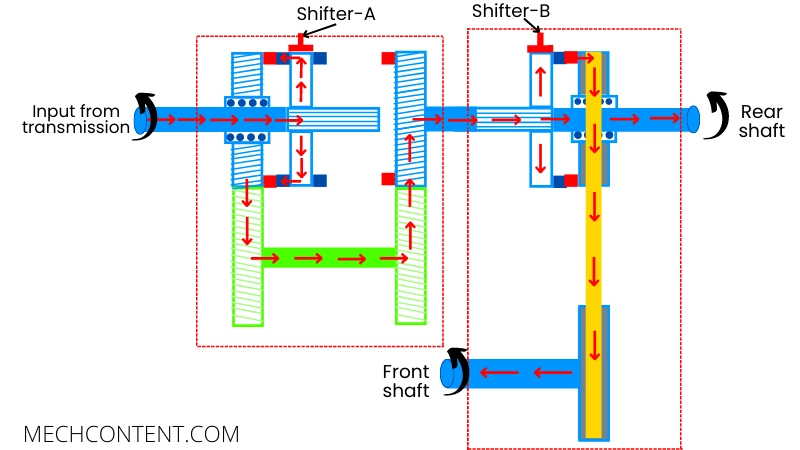
For this purpose, the shifter mechanism-A connects the input shaft to the left side gear. Thus it reduces the speed of the output shaft.
The shifter mechanism-B connects the rear output shaft with the chain sprocket. Therefore the front shaft also rotates along with the rear shaft.
This 4L mode is suitable for driving a vehicle on slippery roads or moving on muddy roads.
C] 4H (4 wheel drive at high-speed ratio):
In this mode, the transfer case transmits the power to the front and rear wheels at a higher speed ratio.
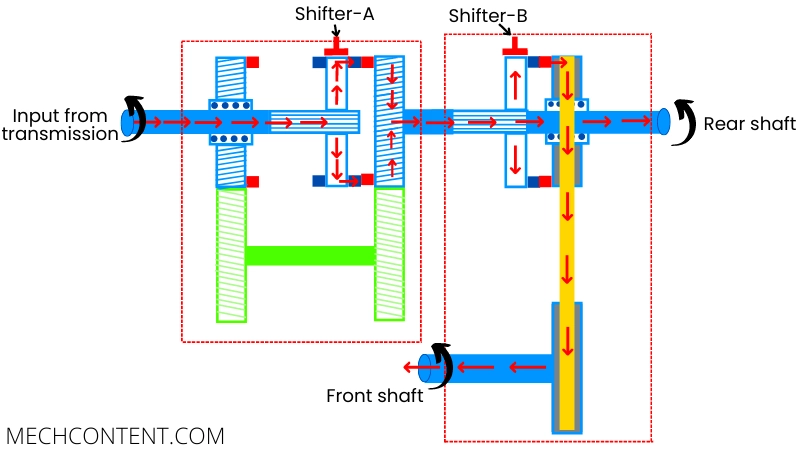
For this purpose, the shifter mechanism-A connects the input shaft to the right-side gear, Thus the output shaft rotates at the same speed as the input shaft.
The shifter mechanism-B connects the rear output shaft with the chain sprocket, thus the power is transmitted to both front and rear wheels.
This mode of the transfer case is suitable for driving on wet roads at high speed.
D] Neutral:
In neural mode the shifter mechanism-A never connects with any gear, thus the power never gets transmitted further.
Therefore based on the road conditions, the driver can select any drive mode of the transfer case while driving.
Types of transfer case:
There are different criteria are used for the classification of transfer cases:-
Based on the drive used:-
Based on the type of drive used for transmitting power to the front output shaft, the transfer cases are classified as follows,
[i] Chain driven transfer case:
This type of transfer case uses a chain drive to transfer power from the rear output shaft to the front output shaft.
This type of transfer case is less noisy and used in most light-duty vehicles like passenger cars, pick-ups, SUVs, etc.
[ii] Gear-driven transfer case:
This type of transfer case uses a set of gears to transmit the power from the rear output shaft to the front output shaft.
This transfer case has a higher strength than the chain-driven transfer case and hence it is used in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks. This transfer case is heavier than the chain drive transfer case and also creates more noise.
Based on the housing of transfer case:-
Based on the housing, the transfer case has the following two types:-
[i] Married transfer case: The married type of transfer case is directly bolted onto the transmission unit of the vehicle.
[ii] Divorced transfer case: In this type, the transfer case is placed independently and connected to the transmission through a short shaft.
Transfer case vs Transmission:
| Sr.No. | Transfer case | Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | It is used to split the power from the transmission to the front drive shaft and rear drive shaft. | The transmission is a reduction gearbox that allows you to drive a vehicle at various speed steps. |
| 2 | It is mounted after the transmission. | It is mounted after the engine and connected with the help of a clutch/torque converter. |
| 3 | It is necessary for the 4-wheel drive vehicle. | It is necessary for 2-wheel drive and 4-wheel drive vehicles. |
What is transfer case oil?
Transfer case oil is the fluid used in the transfer case to cool and lubricate the bearing, gears, and other components of a transfer case. The transfer cases use an oil pump to spray the oil on its components at high pressure.
Some transfer cases use gear oil or the ATF fluid (Automatic transmission fluid) while some of the transfer cases use a special fluid for lubrication.
Bad transfer case symptoms:
Following are some of the symptoms of the bad transfer case:
- Difficulty while shifting gear that causes due to the insufficient transfer case oil.
- Oil leakage underneath the transfer case because of the failure of gaskets.
- Grinding noise from the transfer case.
- The vehicle suddenly changes its mode from the 4WD to 2WD or from 2WD to 4WD.
- Difficult to change from the 2WD to 4WD or vice versa.
- 4WD warning light becomes on.
FAQs:
-
Is transfer case same as transmission?
No, the transfer case is a different component used in the 4 wheel drive vehicles.
-
What’s the purpose of a transfer case?
In 4-wheel drive vehicles, the transfer case is used to transmit the power from the transmission output shaft to the rear propeller shaft and front propeller shaft.
-
What cars have transfer cases?
The 4-wheel drive vehicles have a transfer case to drive all wheels.
-
Does an AWD vehicle have a transfer case?
Yes, the all-wheel-drive (AWD) vehicles have a transfer case.
-
Do 2WD vehicles have a transfer case?
The vehicles that run only in 2-wheel drive mode don’t have a transfer case.
-
What happens when transfer case goes out?
When the transfer case goes out, then the vehicle shows some of the following symptoms,
The abnormal noise from the transfer case
The drive mode changes automatically from 4WD to 2WD.
It becomes difficult to change the drive mode. -
Can you drive with a broken transfer case?
Driving the vehicle with a broken transfer case can also damage other components of the vehicle drivetrain.
Hence, In this blog post, we explained every element of the transfer case in great depth. Please ask any concerns you may have regarding this blog post in the discussion area below.
Media credits:
- Transfer case image by BUILD2