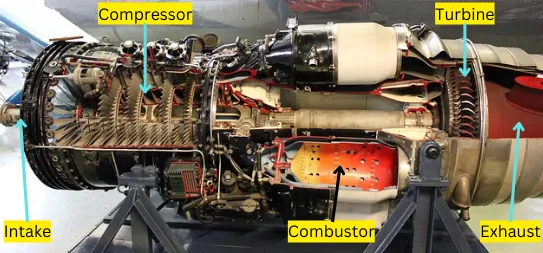
What is a Gas turbine?
Gas turbine is a continuous internal combustion engine that works on the principle of a Brayton cycle. In this flow of working gas continuously goes through the different processes that are Compression, Combustion, and Expansion.
The gas turbine was founded by John Barber in 1791.
It has lower weight-to-power ratio as compared to other power plants, hence they are smaller in size as compared to other power plants.
Contents:
Working cycle:
The gas turbine works on the Brayton cycle.
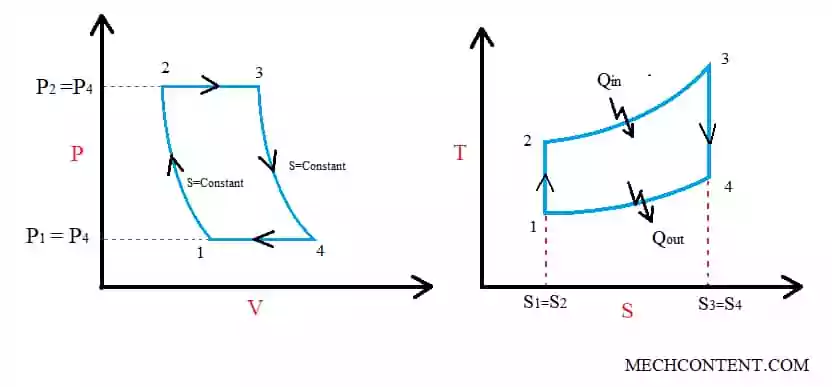
Brayton cycle consists of two isobaric and two isentropic processes.
1-2:- Isentropic compression, pressure increases from P1 to P2.
2-3:- Constant pressure heat addition process
3-4:- Isentropic/Reversible adiabatic expansion
4-1:- Constant pressure heat rejection process
Classification of Gas turbine:
There are two types of the gas turbine: Open cycle gas turbine, Closed cycle gas turbine
Let’s discuss each of them.
A) Open cycle gas turbine:
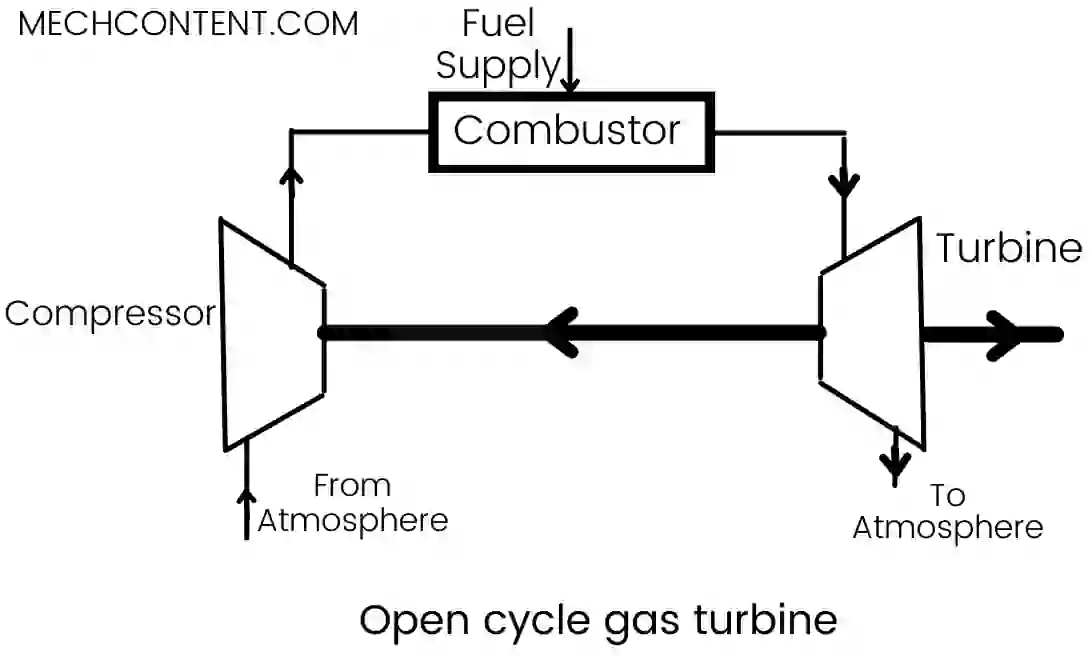
Open cycle gas turbine uses atmospheric air as a working gas, and it consists of the three main components: axial flow air compressor, combustor or combustion chamber, and turbine.
Working:
The air compressor takes the air from the atmosphere and compresses it to high pressure and temperature.
This compressed air then enters the combustion chamber, where fuel directly mixes with the high-pressure air. Therefore, fuel combustion takes place inside the combustion chamber.
The high-pressure hot gases from combustion are expanded into the turbine and then release into the atmosphere. Due to the expansion of high pressure hot gases over the turbine blades, power is obtained at the turbine.
As compressor and turbine are mounter on the same shaft, some turbine work is utilized to run the compressor. Thus, the net-work on the output shaft becomes,
Net-work obtained = Wn = Wt – Wc
Where
Wt = Work developed by the turbine
Wc = Work to drive compressor
B) Closed cycle gas turbine:
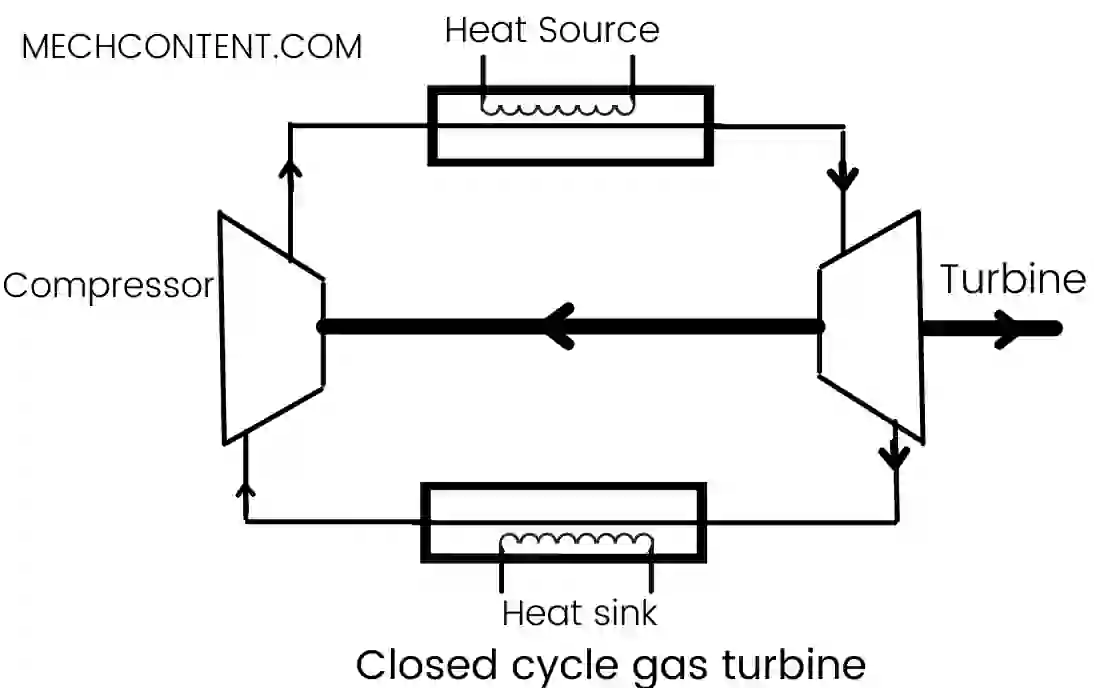
Closed cycle gas turbine consists of the four main components: axial flow compressor, heat source, turbine, and heat sink.
Working gas used in this gas turbine has more specific heat and properties better than atmospheric air (helium, and argon gases). But these gases are costly, hence needs a closed system for circulation.
As compared to open cycle gas turbine, in a closed cycle extra components used that are the heat sink and heating source.
The heating source is provided to heat the gas, while the heat sink is heat exchangers that absorb the heat from hot working gas after expansion from the turbine.
Working:
The compressor takes the gas from the heat sink and compresses it to high pressure and temperature.
The compressed gas from the compressor enters the heating source, where the gases gain heat to increase its pressure and temperature. The high-pressure hot gases are expanded over turbine blades.
Due to expansion of gases in the turbine, power is obtained at the turbine shaft. Some portion of this power is used to drive the compressor. For that, compressor and turbine are located onto the same shaft.
The low pressure gas from the turbine further enters the heat sink, where it loses heat to the sink to become cool. Again these gases enters the compressor and the cycle repeats.
In such a way, this cycle continues again and again to generate power.
Methods to improve the efficiency of the gas turbine:
To improve gas turbine efficiency, there are 3 methods as follows:
1] Reheating in gas turbine: In this method, the low pressure gases from the main turbine are again heated in reheater to increase its pressure and temperature. After reheating, these gases are expanded into the another low pressure turbine.
2] Intercooling in gas turbine: In this method, the compression is done in two steps with intercooling to lower the compression work.
After compression in the first compressor, the gas is cooled in an intercooler and enters the another compressor for more compression.
3] Regeneration in gas turbine: In this method, the amount of heat lost in turbine exhaust is utilized to heat the gases before the combustion chamber.
Gas turbine formulae:
Following are the formulae to find various quantities related to the gas turbine.
1] Work to drive compressor:
Wc = m Cp (T2-T1)
Where
T1 = Input air/gas temperature
T2 = Compressed air temperature
Cp = Specific heat of air/gas
m = mass of air/gas
2] Turbine work:
Wt = m Cp ( T3-T4)
Where,
T3 = Temperature of air pressure at the entry of turbine
T2 = Temperature of air pressure at the exit of the turbine
Cp = Specific heat of air/gas
m = mass of air/gas
3] Net Work:
Wn = Wt – Wc
4] Heat supplied:
Qs = m cp (T3-T2)
5] Gas turbine efficiency:
`\eta=\frac{Wn}{Qs}=\frac{Wt – Wc}{Qs}`
6] Work ratio of gas turbine:
W.R. = `frac{Wn}{Wt}= frac{Wt-Wc}{Wt}=1-frac{Wc}{Wt}`
7] Back work ratio of gas turbine:
B.W.R. = `\frac{Wc}{Wt}`
Advantages of Gas turbine:
Gas turbines are used because of the following advantages:
- It is smaller in size.
- It has a Lower weight per power developed
- No vibration occurs.
- It can be used where problems of water availability.
- Simple in operation.
- Easy installation.
- It occupies less space, hence we can use it where the unavailability of a large area.
- Low Maintenance.
Applications of Gas turbine:
The gas turbine is used in the following applications:
- Marine and transport application
- In the Aircraft
- In the Military applications
- Turbocharging in diesel plants.