Scavenging in engine is necessary process for the effective combustion of fuel that leads to better fuel efficiency, and power output. In this article we are discussing the scavenging process occurs in two stroke and four stroke engines.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- What is Scavenging in IC engine?
1.1. Scavenging in two stroke engines:
1.2. Scavenging in four stroke engines:
1.3. Scavenging efficiency: - Why is Scavenging necessary in an engine?
- Types of Scavenging in two stroke IC engines:
3.1. Uniflow scavenging:
3.2. Cross-flow scavenging:
3.3. Loop or Reverse scavenging:
What is Scavenging in IC engine?
Scavenging in IC engine is the process of replacing the burnt gases from the previous combustion cycle in the cylinder by the fresh charge/air for the next combustion cycle.
The good scavenging process is significant for proper fuel combustion and better power output. In ideal case of scavenging, the incoming fresh charge should push the exhaust mass without mixing with it.
Scavenging is an important process as it removes the remaining burnt gases from the engine. Otherwise, if these gases mix with a fresh charge, it causes improper combustion and results in low power output.
If the scavenging process is not done properly in an IC engine, then it causes chances of auto-ignition, decreases the engine efficiency as well reduces the power output.
Scavenging in two stroke engines:
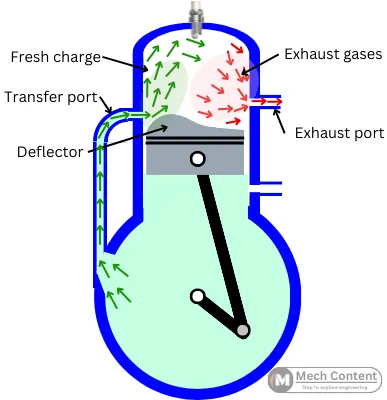
In two stroke engines, two processes happen simultaneously during single stroke. Thus, the time for removal of exhaust gases is very less. Hence there is a higher possibility that the exhaust gases remain inside the cylinder causing dilution of fresh charge. This is a case of poor scavenging.
As shown in the port timing diagram, in two stroke engines for a certain angle of θ, the inlet and exhaust port remain open at the same time. It means, the exhaust process and fresh charge transfer process are carried simultaneously. So, there is a higher chance of loss of fresh charge to the exhaust port.
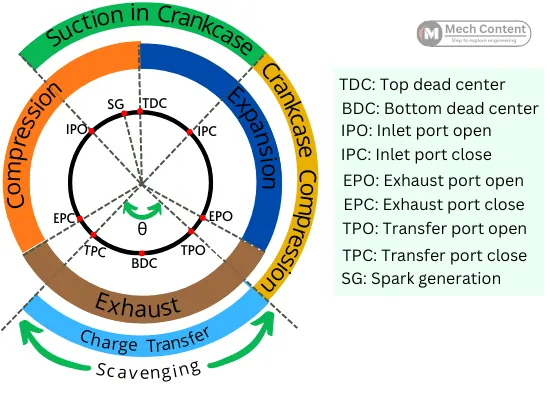
Thus the scavenging in 2-stroke engines is more complicated than the 4-stroke engines.
For the scavenging purpose, the piston crown in two stroke engines has a specific shape called deflector.
The role of deflector is to force the fresh charge in upper direction towards TDC, and directing exhaust gases down toward the exhaust port. This avoids the direct entry of the fresh charge into the exhaust port. Thus, the fresh air remains inside while the exhaust gases go outside.
The different types of scavenging used in two stroke engines are discussed later in this article.
Scavenging in four stroke engines:
In four stroke engines there is a separate exhaust stroke for the removal of exhaust gases. Therefore, the scavenging of the cylinder is done by the piston during the exhaust stroke.
The four-stroke engine also uses valve overlap that effectively boosts the scavenging process. In this process, both intake and exhaust valves kept open for few degrees before the end of exhaust stroke and also few degrees after start of intake stroke.
During this period, the leftover exhaust gases in cylinder are pushed outside by the incoming fresh charge/air.
Scavenging efficiency:
Scavenging efficiency is the term that indicates the ratio of mass of fresh charge retained in cylinder at the time when both valves are closed to the total trapped mass in cylinder.
`\text{Scavenging efficiency}=\frac{\text{Mass of fresh charge retained}}{\text{Trapped mass in cylinder}}`
Why is Scavenging necessary in an engine?
The bad scavenging causes following difficulties in engine:
1] Incomplete combustion next cycle: The bad scavenging causes dilution of fresh charge by mixing it with remaining exhaust gases from last combustion cycle. The dilution of fresh charge causes incomplete combustion of fuel. It results in reduced power and increases emissions.
Scavenging helps in removing all previous combustion gases from the engine and prevents fresh charge dilution.
2] Increased fuel consumption: Due to the loss of fresh charge to the exhaust and due to the dilution of charge, the fuel required to generate unit amount of power increases. It causes an increase in SFC (specific fuel consumption) of engines.
Proper scavenging reduces fuel consumption and loss of fresh charge/air to the exhaust.
3] Low efficiency: Thermal efficiency of engines lowers due to the dilution. The proper engine scavenging increases the power as well as the efficiency of the engine.
4] Overheating: If scavenging is not carried out properly then the average temperature inside the cylinder increases.
To avoid these drawbacks and for efficient operation of engines scavenging is necessary in engines.
Types of Scavenging in two stroke IC engines:
The 3 types of scavenging used in two stroke IC engines are as follows:
- Uniflow scavenging
- Cross-flow scavenging
- Loop or Reverse scavenging
Let’s discuss each of them in detail.
1] Uniflow scavenging:
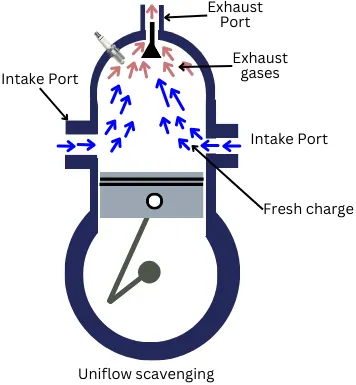
In this scavenging method, one or two intake ports are located at the sides of the cylinder and the exhaust port is located at the cylinder head.
The fresh charge enters from both side intake ports. It flows upwards and pushes the burnt gases to the exhaust valve that is located at the top of cylinder.
This method of scavenging has minimum loss of fresh charge/air and lower fuel consumption. Hence this method gives better engine efficiency as compared to other methods.
Uniflow scavenging can give better scavenging at low speed as well as at high speed. It is commonly used in large-sized two stroke engines such as in two-stroke engines of big marine ships.
2] Cross-flow scavenging:
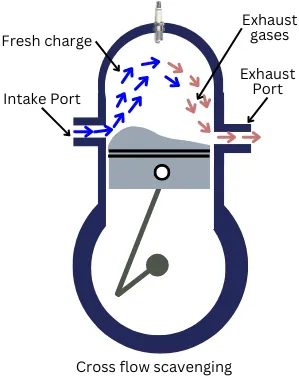
The cross-flow type scavenging has an inlet port and the exhaust port that are located on opposite sides to each other. The deflector piston (hump-shaped piston head) is used in this type of scavenging.
When the fresh charge enters into the engine from the intake port, due to the deflector, the incoming charge moves upwards and pushes the upper burnt gases downside to the exhaust port.
Therefore, the deflector on the piston assists in the engine’s scavenging operation.
This method of scavenging performs well during the low engine speeds while it has poor scavenging at the high engine speeds or at full throttle time.
3] Loop or Reverse scavenging:
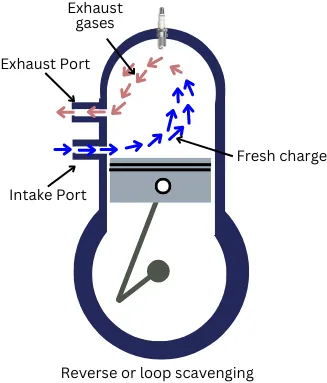
In this scavenging method, the intake port and exhaust ports are located at the same side on the engine cylinder.
In this method, the size of the intake port is large to enter a large volume of charge inside the cylinder, and the size of the exhaust port is small (to increase velocity) to flow out burnt gases quickly.
When the fresh charge enters from the intake port, the fresh charge has a swirling motion (as like a loop). The fresh charge moves upwards and pushes back the burnt gases. Hence in such a way, these burnt gases flow out of the cylinder.
The loop scavenging performs well during high engine speeds.