Without valve overlap, a small amount of exhaust gases will remain in the combustion chamber which will affect the engine’s performance and exhaust. Valve overlap promotes better scavenging of the gases in the engine.
Thus in this article, we are going to learn about valve overlap.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- What is Valve overlap?
- Purpose of Valve overlap:
- What factors impact the amount of valve overlap?
- Formula:
- How to calculate Valve overlap?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Valve overlap:
- FAQs:
What is Valve overlap?
Valve overlap is the degrees of crankshaft rotation during which the intake valve and exhaust valve remain open at the same time. The valve overlap occurs a few degrees before the end of the exhaust stroke or a few degrees after the start of the suction stroke.
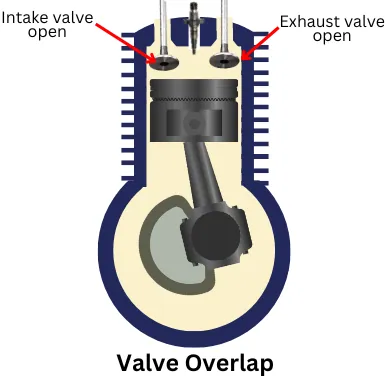
The below figure shows the actual valve timing diagram for a 4-stroke IC engine which indicates the opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves relative to the crankshaft angle.
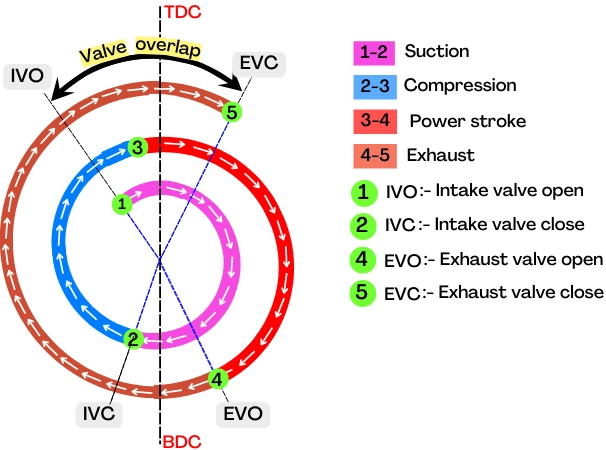
The above figure shows that, the intake valve opens a few degrees before the piston reaches at TDC during the exhaust stroke and the exhaust valve closes a few degrees after the piston starts to move in a downward direction during the suction stroke.
Thus during this period from the opening of the intake valve to the closing of the exhaust valve, both valve remains open at the same time which is known as the valve overlap.
It is measured in terms of an angle turned by a crankshaft from the opening of the intake valve to the closing of the exhaust valve.
Purpose of Valve overlap:
There are the following purposes:
1] It promotes scavenging:
The piston does not go above the TDC of the cylinder, thus the piston itself can’t push out the exhaust gases in the region of clearance volume.
Due to the flow of exhaust gases, a small low-pressure region is created above the piston head. During the valve overlap, the fresh intake charge fills this low-pressure region and helps to expel the exhaust gases completely.
2] Avoid dilution of charge:
Without valve overlap, some portion of exhaust gases remains in the cylinder. During the suction stroke, these gases mix with the intake charge and dilute the fresh mixture.
As the valve overlap helps to expel out the maximum amount of exhaust gases, thus it helps to avoid the dilution of the air-fuel mixture.
3] Cooling of exhaust valve: The overlap also helps to cool the exhaust valve.
What factors impact the amount of valve overlap?
The amount of overlap depends on the following factors:
1] Speed of engine:
The engines running at higher speeds (e.g., Sports cars) require a larger angle of valve overlap so that, the engine will get enough time for scavenging at a higher speed.
While the engine running at lower rpm (e.g., street cars) can get enough time for scavenging at a lower valve overlap angle.
2] Number of valves present in cylinder head:
As the 4-valve engine has more intake and exhaust flow than the 2-valve engine, thus the 4-valve engine requires less valve overlap than the 2-valve engine.
3] Loss of intake mixture:
The excessive valve overlap causes loss of intake mixture through the exhaust valve. Therefore the maximum overlap should be optimized to avoid the loss of fresh intake mixture.
Formula:
If the crankshaft angle during the opening of the intake valve and closing of the exhaust valve is known, then in this case the valve overlap is given by,
valve overlap = Angle turned by a crankshaft from IVO to EVC
Valve overlap = [Angle between IVO and TDC] + [Angle between EVC and TDC]
Where,
IVO = Intake valve open
EVC = Exhaust valve closes
TDC = Top dead center
If the intake duration and exhaust duration (in terms of crankshaft angle) and the lobe separation angle (discussed below) are known, then the valve overlap is given by,
`\mathbf{\text{Valve overlap} = \frac{\text{Intake duration + Exhaust duration}}{2}- 2(\text{Lobe separation angle})}`
How to calculate Valve overlap?
It can be calculated by using the following two methods:
1] From valve timing diagram:
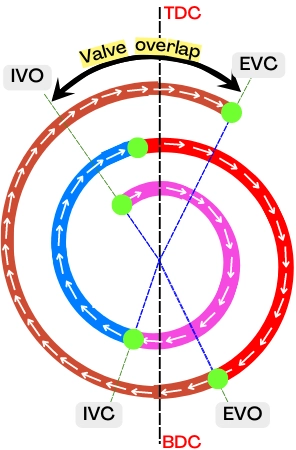
For the above valve timing diagram, the valve overlap (VO) is measured as follows,
VO = [Angle between IVO & TDC] + [Angle between EVC & TDC]
Example: Consider for the particular engine, the intake and exhaust valve operates as follows:
Intake valve open (IVO): 24° before TDC
Intake valve closes (IVC): 50° after BDC
Exhaust valve opens (EVO): 60° before BDC
Exhaust valve closes (EVC): 20° after TDC
For the above information, the valve timing diagram is as follows:
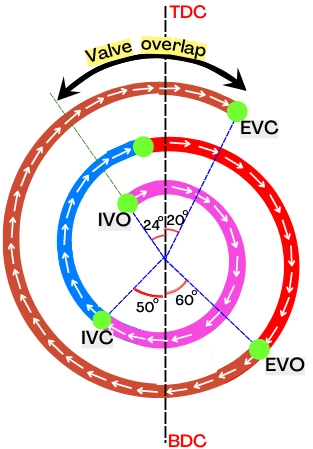
Thus the valve overlap (VO) is given by,
= [Angle between IVO & TDC] + [Angle between EVC & TDC]
= 24° + 20°
VO = 44°
2] From lobe separation angle, Intake and Exhaust duration:
The below figure shows the position of the cam lobes of intake and exhaust valves.
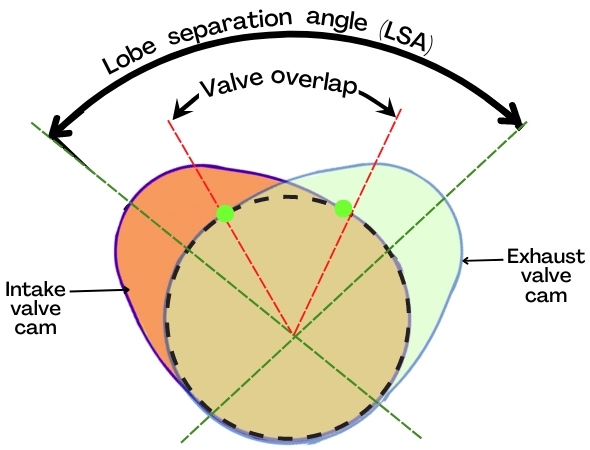
The lobe separation angle [LSA] is the angle between the centerline of the intake valve lobe and the centerline of the exhaust valve lobe.
In this case, the valve overlap (VO) is given by,
`\text{VO} =\frac{\text{Intake duration + Exhaust duration}}{2}- 2[\text{LSA}]`
Where,
Intake duration = Angle turned by the crankshaft during the period of the intake valve open
Exhaust duration = Angle turned by the crankshaft during the period of the exhaust valve open
Example:
Consider an engine with the following specifications:
Intake Duration: 254°
Exhaust Duration: 260°
Cam lobe separation angle [LSA]: 110°
Thus, in this case, the valve overlap (VO) is given by,
`=\frac{\text{Intake duration + Exhaust duration}}{2}- 2[\text{LSA}]`
`= \frac{254^{\circ}+260^{\circ}}{2}- 2(110°)`
VO = 37°
Advantages and Disadvantages of Valve overlap:
The advantages are as follows:
- It promotes scavenging.
- It helps to increase the intake of fresh charge at high engine speed which increases the high-end power of the vehicle.
- It helps in cooling of the exhaust valves.
The disadvantages are as follows:
- At lower speed, the engine creates less vacuum in the intake manifold, which affects the power brake system, Therefore the brake pedal feels harder.
- The valve overlap is not used for the engine running at low rpm because of poor low-end power.
- The excess overlapping causes loss of fresh intake charge through the exhaust valve.
FAQs:
-
What is the cause of Valve overlap?
It occurs because of the early opening of the intake valve before the piston reaches TDC and the late closing of the exhaust valve after the piston reaches TDC.
-
When does Engine Valve overlap happen?
It occurs at the end of the exhaust stroke and during the initial period of the intake stroke.
-
Why is engine valve overlap is significant?
It helps to increase the high-end power output of the engine by feeding more intake charge into the engine.
-
What are the two purposes of valve overlap?
These are the main purpose of valve overlap:
a] Avoid dilution of fresh charge
b] To fill maximum fresh charge in the cylinder. -
How to identify valve overlapping in the engine?
Check the movement of the valve by slowly rotating the engine. If the intake valve starts to open before the complete closing of the exhaust valve, then there is a valve overlap.
-
What mean by negative valve overlap?
Negative valve overlap indicates early closing of the exhaust valve and late opening of the intake valve.