What is Intercooling in gas turbine?
Intercooling in gas turbine is one of the method to improves the efficiency of the gas turbine. In this method, the net work output is increased by reducing the work required to drive the compressor.
This is done by carry out the compression of air in two stages.
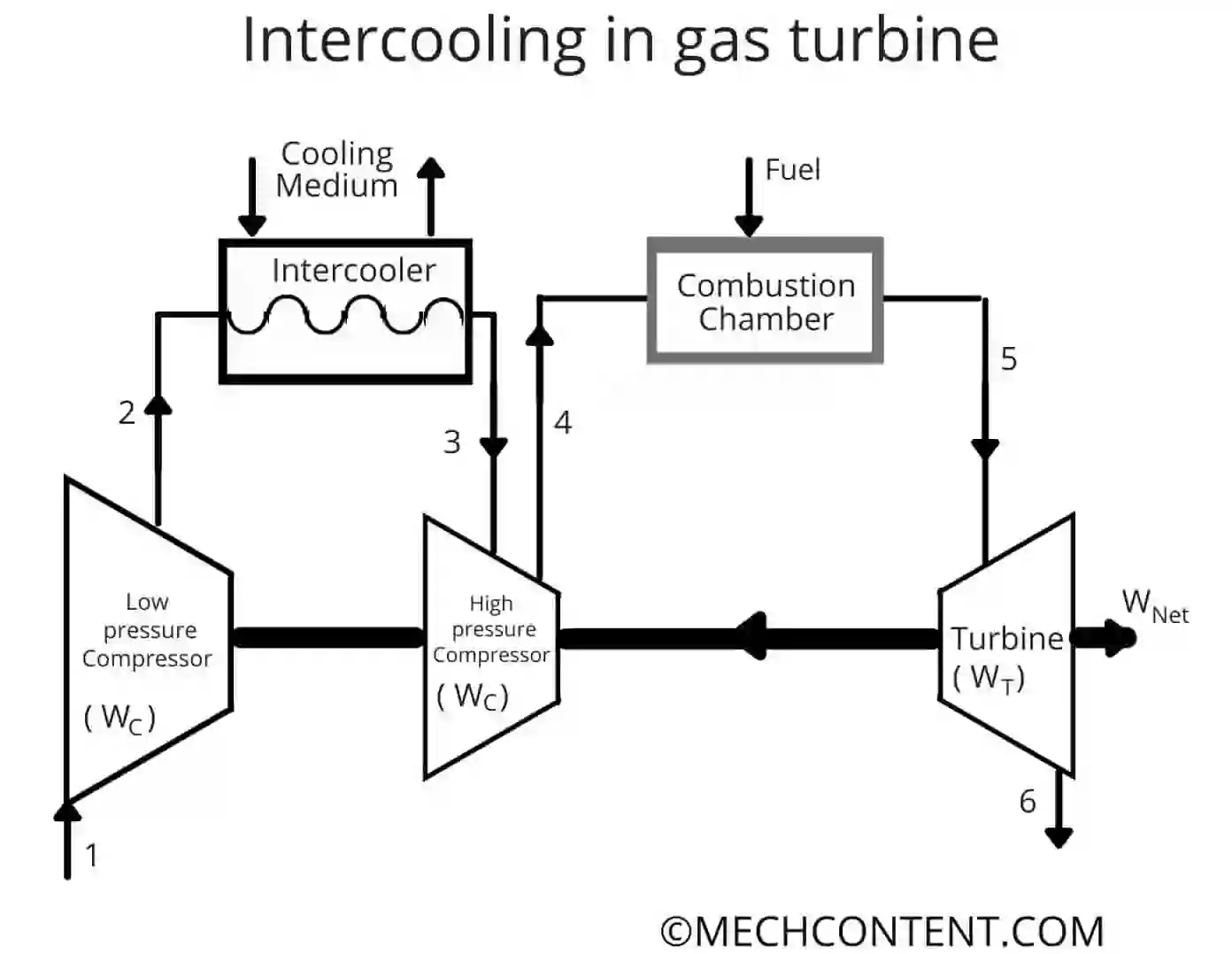
In the gas turbine, the large amount of work developed by the turbine is utilized to run the compressor. In this method, multiple compressors are used for compression and the intercooler (Heat Exchanger) to cool the air to avoid overheating.
Effect of intercooling in gas turbine:
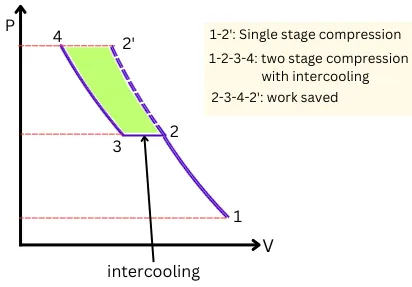
The below figure shows the PV graph for the compression process in single stage (1-2′) and in two stages with intermediate intercooling (1-2-3-4).
As shown below, the total work required for compression with intercooling is less than the work required for normal compression.
The area 2-3-4-2′ in the below figure shows the amount of net work saved by performing intercooling between the two stages of compression.
The efficiency of a gas turbine is given by,
`\eta=\frac{\text{Net work}}{Q_{s}}=\frac{W_{T}-W_{C}}{Q_{s}}`
Where
`W_{C}`= Work required to drive compressor
`W_{T}`= Work developed by turbine
`Q_{s}` = Heat supplied
The above equation says, the efficiency is directly proportional to the net work. And the efficiency will increase with decrease in compressor work.
So to increase the net work and efficiency, we need to reduce the work required to drive the compressor.
Hence, instead of using a single compressor, if the compression is done in multistage stages along with intercooling, it will help in reducing work required to drive the compressor.
Also, it will increase the net work and efficiency of the gas turbine.
Read also: