The neutral axis represents the point in a beam’s cross-section where stress is zero. It separates the regions of tensile and compressive stress, remaining stress-free during bending.
Learn about the neutral axis in different beam types, its formulas, and why bending stress is zero at this axis.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- What is the Neutral axis?
- How to find Neutral axis?
2.1. Neutral axis of a simple beam:
2.2. Neutral axis of composite beam: - Neutral axis formulae for different geometric shapes:
- Why bending stress is zero at neutral axis?
- FAQ’S
What is the Neutral axis?
Neutral axis for the beam subjected to bending is a line passing through the cross-section at which the fibres of the beam does not experience any longitudinal stress (compressive or tensile).
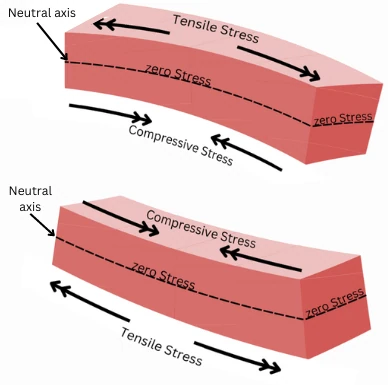
For the above beam, the dotted line indicates the neutral axis.
Due to the bending moment the beam experiences different stresses on either side of neutral axis.
Compressive stress on one side:
For the beam in below figure, the fibres above the neutral axis are subjected to compression.
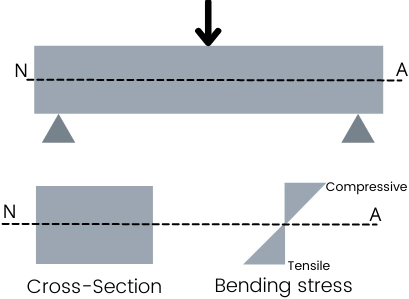
The uppermost fibres of the beam are under higher compressive stress and this compressive bending stress gradually decreases as we move towards the neutral axis and it becomes zero at the neutral axis.
Tensile stress on another side:
For the beam in above figure, the fibres below the neutral axis are subjected to tension.
The bottommost fibre of the beam experiences the highest tensile stress and it gradually decreases as we move toward the neutral axis and it becomes zero at the neutral axis.
No stress at neutral axis:
Therefore the fibres at the neutral axis are not subjected to compression as well as tension. And thus it becomes clear that at the neutral axis the value of bending stress is zero.
How to find Neutral axis?
The method to find a position of the neutral axis is different for simple beam and composite beam:-
A] Neutral axis of a simple beam:
For a simple beam (consists of same material), the neutral axis passes through the centroid of the cross-sectional area. Therefore it can be easily found by calculating the position of the centroid in a vertical direction.
To know about how the Neutral axis is different from Centroid then check our this article.
The position of the neutral axis is given by,
`\bar{y}=\frac{\sum A_{i}y_{i}}{\sum A_{i}}`
B] Neutral axis of composite beam:
The composite beam consists of a different material. The neutral axis of the composite section passes through the centroid of an equivalent cross-section.
To find the neutral axis of such a composite beam, convert the actual cross-section into the equivalent section with the same modulus of elasticity and find the centroid of this equivalent cross-section.
Here are the steps to find the N.A. of composite section.
Step 1: Convert composite cross-section into equivalent cross-section:
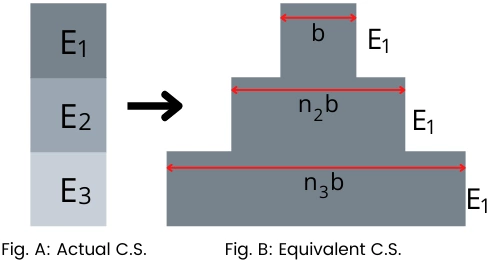
As shown in Fig. A, The cross-section consists of a material with a modulus of elasticity E1, E2, and E3.
To convert the composite section into the equivalent cross-section with an equivalent modulus of elastic of E1.
Multiply the width of section 2 by n2. The new width of section 2 is,
b2 = n1 . b
`\text{Where},\ n_{2} = \frac{E_{2}}{E_{1}}`
Multiply the width of section 3 by n3. The new width of section 3 is,
b3 = n3 . b
`\text{Where},\ n_{3} = \frac{E_{3}}{E_{1}}`
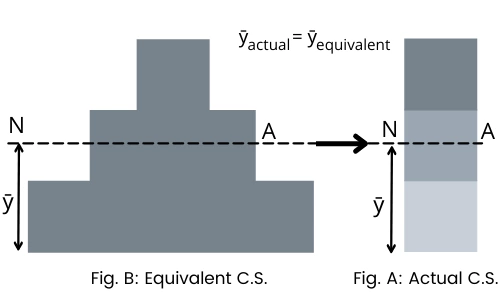
Step 2: Find the position of the neutral axis:
Now by simply finding the centroid of a composite section in a vertical direction, we can find the position of the neutral axis.
`\text{Where},\ \bar{y}_{\text{Composite}}=\bar{y}_{\text{Equivalent}}`
Neutral axis formulae for different geometric shapes:
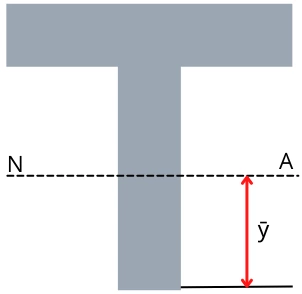
1] Neutral axis of T beam:
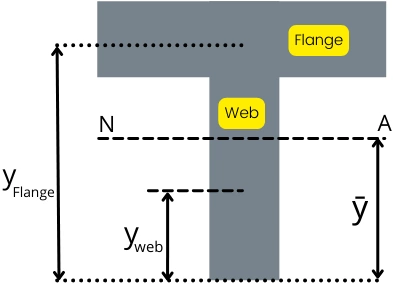
The position of the neutral axis from the bottom of the web is given by,
`\mathbf{\bar{y}=\frac{A_{\text{web}}.y_{\text{web}}+A_{\text{flange}}.y_{\text{flange}}}{A_{\text{web}}+A_{\text{flange}}}}`
Where,
Aweb = Area of the web
Aflange = Area of flange
yweb = Centroid of the web from bottom of web
Aflange = Centroid of the flange from bottom of web
2] Neutral axis of a circle:
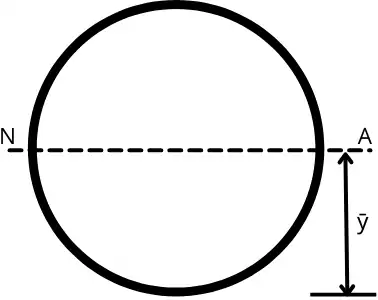
For the circular section, the centroid is at the centre of the circle therefore the neutral axis of the circle is given by,
`\mathbf{\bar{y}=\frac{d}{2}}`
3] Neutral axis of a rectangular beam:
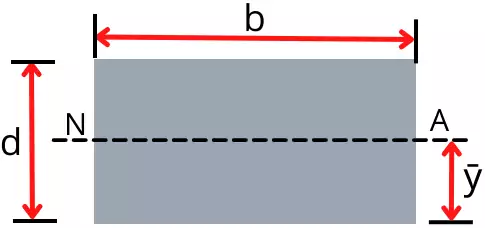
For the rectangular cross-section, the neutral axis passes through the centroid.
Therefore the location of the neutral axis for the rectangular beam is given by,
`\mathbf{\bar{y}=\frac{d}{2}}`
4] Neutral axis of a triangle:
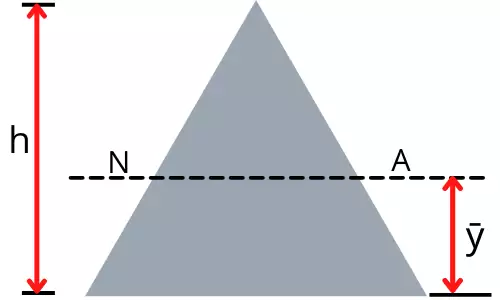
For the equilateral triangular cross-section, the neutral axis passes through the centroid.
Therefore the location of the neutral axis for the equilateral triangle is given by,
`\mathbf{\bar{y}=\frac{h}{3}}`
Why bending stress is zero at neutral axis?
For the beam subjected to the bending, the outermost fibre at one end experiences the highest tensile stress and the outermost fibres at the opposite end experience the highest compressive stress.
Varying Bending Stress:
Therefore for the cross-section of the beam, all the fibres from one of the outermost ends to the opposite outermost end are subjected to varying bending stress from the highest tensile stress to the highest compressive stress.
Transition from Tensile to Compressive Stress:
The bending stress from the highest tensile stress gradually decreases to zero and again gradually increases to the highest compressive stress.
Neutral Axis and Zero Bending Stress:
At a certain location where the bending stress changes its nature from tensile to compressive, the value of the bending stress becomes zero and thus the fibres at this location never experience any bending stress. This position is known as the neutral axis.
Therefore at the neutral axis, the value of the bending stress is zero.
FAQ’s
-
Where is Neutral axis of a beam?
The elastic neutral axis passes through the centroid of the beam cross-section.
-
Does the neutral axis always pass through the centroid?
The elastic neutral axis always passes through the centroid of the cross-section and the plastic neutral axis pass through the line that divides the cross-sectional area into two parts of equal area.
-
What will be bending stress at neutral axis?
The bending stress at the neutral axis is zero since at the neutral axis the bending stress changes its nature from compressive to tensile.