Hello friends, Today we will discuss the Ultrasonic Machining, that depends on ultrasonic wave. But before starting this let’s know what is ultrasonic wave.
It is an inaudible sound wave with high frequency for humans. The frequency of this wave is more than 20 kHz.
Contents:
What is Ultrasonic machining?
Ultrasonic machining is the advanced machining process in which machining carry out with the help of ultrasonic wave vibration combined with abrasive slurry. This ultrasonic vibrations are between the range of 20 kHz-30 kHz.
Ultrasonic machining is one of the non conventional machining process which is used for the machining of hard & brittle materials like glass, carbide etc.
The below figure is the basic structure of the ultrasonic machining process.
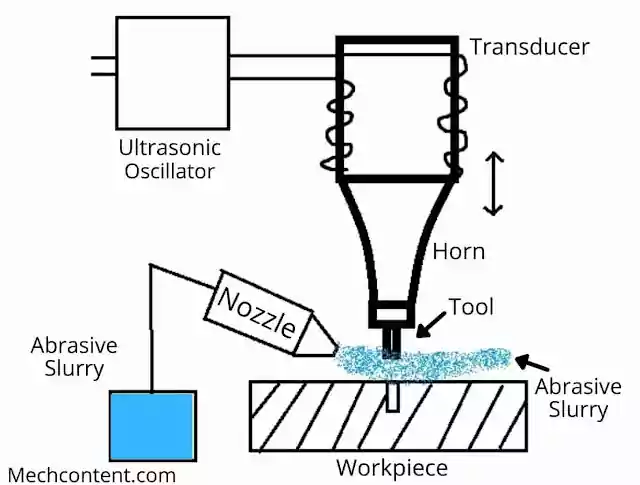
This process is silent process, as it uses the ultrasonic wave that has frequency more than 20 kHz, which is inaudible for humans.
Working principle of ultrasonic machining:
Ultrasonic machining works on the ultrasonic vibrations of tool & abrasive slurry. The tool vibrates at high frequency, more than 20 kHz & this tool impacts on the work-piece surface.
During this hammering action of this tool, abrasive slurry flows between the tool & work-piece surface. This causes brittle fracture and may be a chemical reaction which causes removal of material from the work-piece surface.
Construction:
This machining setup consists of the following components:-
1) Ultrasonic Oscillator :- Ultrasonic oscillator uses the electric energy to generate ultrasonic frequency which further sends to the transducer.
2) Transducer :- Transducer is a device which converts one form of energy to another form. It converts received ultrasonic frequency from ultrasonic oscillator to mechanical vibration.
3) Horn :- The vibration amplitude produced by the transducer is not sufficient for the machining. Hence, a horn is used which increases the vibration amplitude. The horn also holds the tool.
4) Tool :- Tool is attached to the horn. The tool has the same shape as that of the cavity or hole to be produce onto the work-piece surface. This tool is made of the soft material.
5) Nozzle :- The purpose of the nozzle is to supply the abrasive slurry to the space between the tool and work-piece surface.
6) Abrasive slurry :- Abrasive slurry is a mixture of the water and the abrasives. The abrasives used are boron carbide, silicon carbide etc.
Working of ultrasonic machining:
When the power supply gets on, the ultrasonic oscillator starts sending the ultrasonic frequency to the transducer.
The transducer takes this ultrasonic frequency from the ultrasonic oscillator and starts producing the vibration.
When the transducer starts vibrating, the horn and tool also starts vibrating. The horn increases the amplitude of this vibration from the transducer.
Due to this ultrasonic vibration, the tool starts impacting on the workpiece and the abrasive slurry from nozzle starts flows between the tool & work-piece surface.
Hence, due to this hammering action on the abrasive slurry causes the brittle fracture as well the chemical reaction or corrosion which causes removes the material from the work-piece surface.
Advantages of ultrasonic machining:
- High machining accuracy.
- It can be drill different shapes of hole.
- The ultrasonic machine can be handled by the semi-skilled operator.
- It can be used for the conducting & semiconducting material work-piece.
Disadvantages of ultrasonic machining:
- large surfaces can’t machine since it is limited to small size surfaces.
- Less material removal rate (MRR).
- Tool has shorter life due to the ultrasonic wave vibration.
Application of the ultrasonic machining:
This machining process is used in following applications:
- In machining of the brittle materials such as glass, carbide.
- For drilling holes of any shapes.
- For the making slots onto hard material.
- In step drilling of the work-piece.
Read also: