What is a Diaphragm clutch?
A diaphragm clutch is one of the types of automobile clutch that uses the diaphragm spring for the engagement & disengagement of the clutch.
As compared to plate type clutch, In diaphragm clutch, the Diaphragm spring is used in place of the coil spring to keep axial force (Clamping force) on a pressure plate.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- Working principle:
- Construction:
- Diaphragm clutch working:
- Diaphragm clutch advantages and disadvantages:
- Applications:
- FAQs:
Working principle:
The diaphragm clutch works on the Friction principle.
Friction is responsible for the power (Torque) transmission from the Flywheel to the Gearbox.
A Plate with Friction lining on its surface is known as a Friction Plate. The friction Plate is pressed onto the Flywheel under the axial force applied by a pressure plate.
In the Engaged Condition of the Clutch, Flywheel, Friction Plate, and pressure plate are united due to Axial Force exerted by a Pressure plate.
Construction:
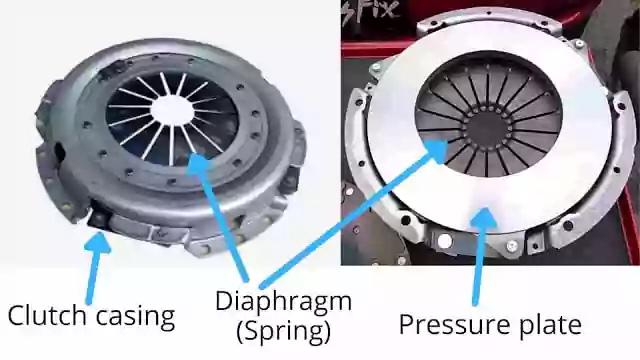
It consists of a friction plate/clutch plate, pressure plate, diaphragm, flywheel, release bearing, clutch pedal, and release fork.
1) Pressure Plate: This plate is used in the clutch to force the friction plate onto the flywheel. The force is applied by the diaphragm located on one side of the pressure plate.
2) Flywheel: Flywheel is connected to the vehicle engine crankshaft and rotates with it. In the running condition (engaged condition), the pressure plate forces the friction plate onto the flywheel.
Due to friction between the friction plate and flywheel, the flywheel and pressure plate rotates together. Thus it results in power transmission from the flywheel to the output clutch shaft.
3) Diaphragm: Diaphragm is one of the types of springs which has a circular shape. It helps to build the pressure on a friction plate.
When the release bearing presses the middle part of the diaphragm, the part of the diaphragm at its circumference moves outwards and presses the friction plate on the flywheel.
4) Friction Plate: This plate is generally located between the flywheel and pressure plate with friction material on both sides surfaces. The friction material is responsible for ensuring engagement between shafts for power transmission.
5) Release Fork: The release fork performs work to press the release-bearing to press the Diaphragm spring. The Release Fork is Connected to the Clutch Pedal through Linkage.
6) Release Bearing: It is a bearing that is operated by the release fork to press the diaphragm spring.
7) Clutch Pedal: The clutch pedal is the pedal that is connected to the clutch and operated by the driver.
Diaphragm clutch working:
Let’s understand the working of the diaphragm clutch in engage and disengage positions with the help of diagrams.
DISENGAGEMENT:
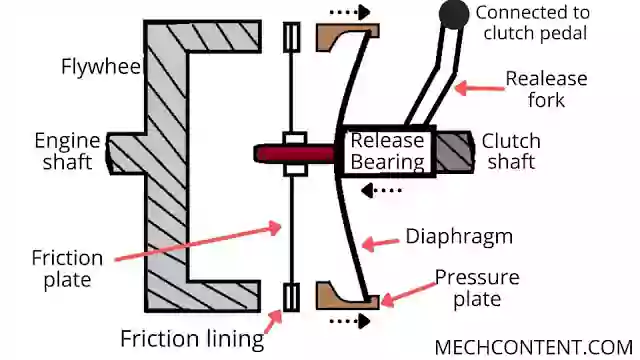
When the driver presses the clutch pedal through a linkages release fork presses the release bearing.
Due to the release Fork presses the release bearing, Release Bearing presses the middle portion of the diaphragm to move inwards.
Due to the inwards movement of the middle portion of the diaphragm, the outside part of the diaphragm moves backward as well as pressure plate also moves backward.
Therefore due to the pressure plate’s backward movement, pressure on the friction plate gets removed. So there is no friction between the plates & flywheel. Hence no power transmission takes place. Hence clutch gets Disengaged.
ENGAGEMENT:
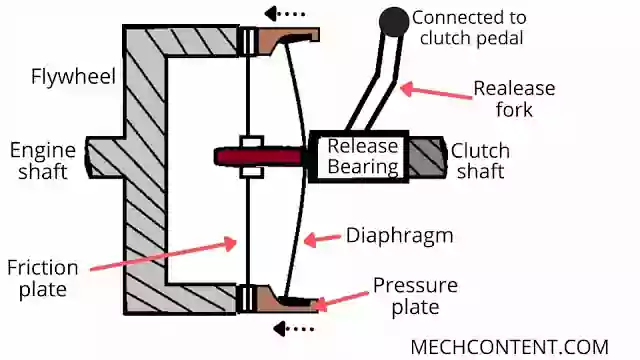
When the driver releases the clutch pedal, it results in the diaphragm again coming to its original position.
Hence outer part of the diaphragm moves towards the left & presses the pressure plate on the friction plate & flywheel. Therefore friction between them causes them to rotate all components together.
Hence power/torque again starts to transmit from the flywheel to the clutch shaft. And the Clutch is said to be in Engaged condition.
Diaphragm clutch advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:-
- It is lighter in weight.
- It has a compact size.
- Diaphragm spring applies more force hence it has a higher torque transmission capacity.
- It has fewer rotating parts hence no problem of noisy working.
- It has dynamic balancing even at high speed.
Disadvantages:-
- For heavy vehicles, the size of the clutch becomes higher for increasing friction surfaces.
Applications:
The diaphragm clutch has the applications in following vehicles:-
- Maruri suzuki swift
- Tata safari Storme
- Ford Ecosport
- Nissan navara
FAQs:
-
How does a Diaphragm clutch work?
The working of the diaphragm clutch depends on the diaphragm spring used in this clutch.
The diaphragm spring maintains the pressure between the flywheel, friction plate, and pressure plate (During engaged condition).
Pressing the diaphragm clutch in the middle causes releasing the pressure on the friction plate. It causes the cluch to disengage. -
What are the advantages of a Diaphragm clutch?
It has the advantage of lightweight as well as dynamic balancing even at high speed.
Read about other types of clutch:
| Single plate clutch | Multiplate Clutch |
| Cone clutch | Centrifugal Clutch |
| Hydraulic Clutch | Vacuum Operated Clutch |
| Electromagnetic Clutch |
Media credits:
- Pressure plate image by ChrisFix.