What is section modulus?
Section modulus is the property of the cross-section that is used while the design of beams. It measures the strength of a beam’s cross-section.
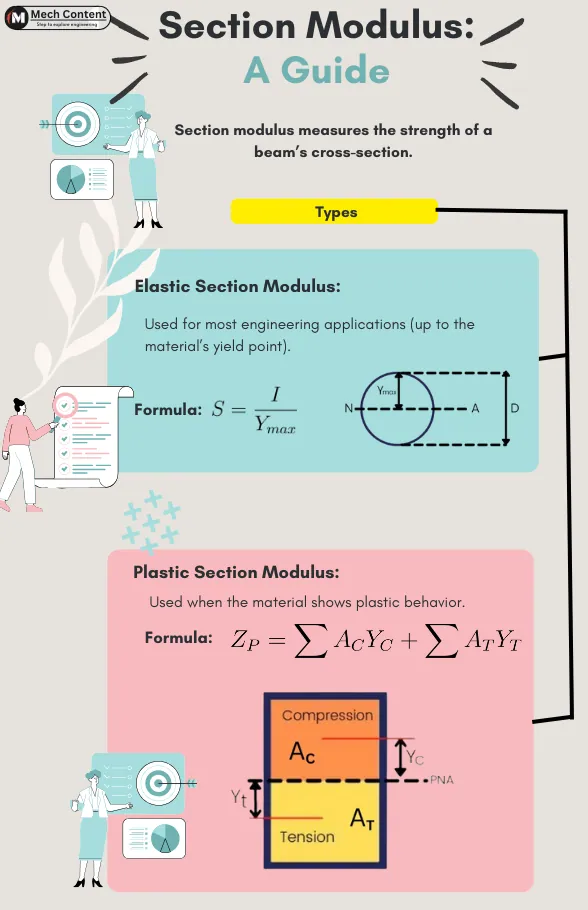
Types of Section Modulus:
The section modulus is classified into two types:
1] Elastic section modulus: The elastic section modulus is applicable up to the yield point of material.
It is used in most engineering applications.
2] Plastic section modulus: The plastic section modulus is generally used for material in which plastic behavior is observed.
In this article, we’re going to discuss:
- Elastic section modulus:
- Plastic section modulus:
- Section modulus units
Elastic Section Modulus:
Elastic section modulus is the ratio of moment of inertia about a neutral axis(`I_{N.A.}`) and the maximum distance between the neutral axis and outermost fiber of beam (`Y_{max}`).
Equation:
The formula of elastic section modulus is given by,
`S = \frac{I_{N.A.}}{Y_{max}}`
Where,
I = Moment of inertia (`m^{4}`)
Ymax = Distance between neutral axes and outermost fiber (m)
Steps to Calculate Elastic Section Modulus:
- Find location of centroid of given cross section.
- Find moment of inertia about neutral axis (`I_{NA}`)
- Find `Y_{max}` from neutral axis.
- Find elastic section modulus using the formula provided above.
Elastic Section Modulus for Different Sections:
1] Circular Section:
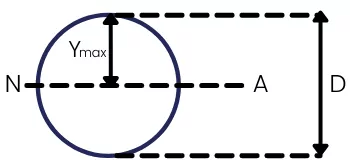
`S_{\text{Circle}}` =`\frac{\pi.D^{3}}{32}`
How to get this…
The moment of inertia about Neutral axes for a circular section is,
`I_{N.A.}`=`\frac{\pi D^{4}}{64}`
The `Y_{max}` is given by,
`Y_{max}`=`\frac{D}{2}`
The elastic section modulus for circular section is,
S = `\frac{I_{NA}}{Y_{max}}`=`\frac{\frac{\pi.D^{4}}{64}}{\frac{D}{2}}`=`\frac{\pi.D^{3}}{32}`
`\mathbf{S_{\text{Circle}} = \frac{\pi.D^{3}}{32}}`
2] Rectangular section:
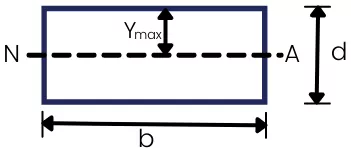
S = `\frac{bd^{2}}{6}`
How to get this…
The moment of inertia about N.A. is given by,
`I_{NA}` =`\frac{bd^{3}}{12}`
The `Y_{max}` is given by,
`Y_{max}` =`\frac{d}{2}`
The elasic section modulus for rectangular section is given by,
S = `\frac{I_{NA}}{Y_{max}}`=`\frac{\frac{bd^{3} }{12}}{\frac{d}{2}}`=`\frac{bd^{2}}{6}`
`\mathbf{S=\frac{bd^{2}}{6}}`
3] Elastic section modulus of hollow rectangle:
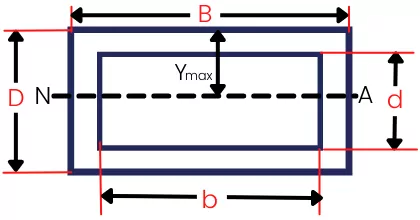
`S_{\text{Hollow rectangle}}` = `\frac{BD^{2}}{6}-\frac{bd^{3}}{6D}`
How to get this…
The Moment of inertia about a neutral axis is given by,
`I_{NA}` =`\frac{BD^{3}}{12}`-`\frac{bd^{3}}{12}`
The `Y_{max}` is given by,
`Y_{max}` =`\frac{D}{2}`
The elastic section modulus for hollow rectangle is given by,
S = `\frac{I_{NA}}{Y_{max}}`=`\frac{\frac{BD^{3} }{12}-\frac{bd^{3} }{12}}{\frac{D}{2}}`
`\mathbf{S =\frac{BD^{2}}{6}-\frac{bd^{3}}{6D}}`
4] Elastic section modulus of square tube:
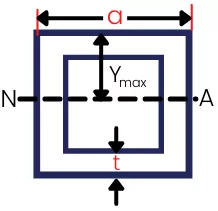
`S_{\text{Square tube}}` = `\frac{a^{3}}{6}`-`\frac{(a-2t)^{4}}{6a}`
How to get this…
The moment of inertia about the neutral axis is given by,
`I_{N.A.}`=`\frac{a^{4}}{12}`-`\frac{(a-2t)^{4}}{12}`
`Y_{max}` is given by,
`Y_{max}` = `\frac{a}{2}`
Now the section modulus for square tube is given by,
S =`\frac{I_{N.A.}}{Y_{max}}`=`\frac{\frac{a^{4}}{12}-\frac{(a-2t)^4}{12}}{\frac{a}{2}}`
`\mathbf{S=\frac{a^{3}}{6}-\frac{(a-2t)^{4}}{6a}}`
Plastic section modulus:
The plastic section modulus is necessary to calculate plastic moment capacity of the section.
The plastic section modulus is the sum of moment of area of area under compression about PNA (plastic neutral axis) and the moment of area of area under tensile stress.
Plastic section modulus equation:
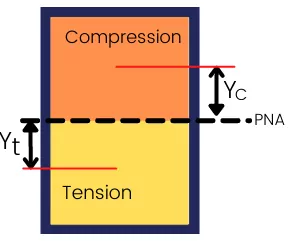
For the above cross-section, the plastic section modulus is given by,
`Z_{P}`=`\sum A_{C}Y_{C}`+`\sum A_{T}Y_{T}`
Where,
AC = Area of cross-section under compression.
AT = Area of cross-section under tension.
YC = Distance from PNA to CG of the areas under compression.
YT = Distance from PND to CG of areas under tension.
Steps to calculate plastic section modulus:
Step 1] Locate the plastic neutral axis.
At the neutral axis, the Area under compression is equal to the area under tension.
`A_{C}` = `A_{T}`
By using this relation, we can find the position of the plastic neutral axis.
Step 2] Find the summation of the product of area of section undergoing compression and the distance of its CG from PNA that is `\sum A_{C}Y_{C}`.
Step 3] Find the summation of the product of the area of cross-section undergoing tension and distance between CG of that area from PNA that is `\sum A_{T}Y_{T}`.
Step 4] Find the plastic section modulus using the formula.
Plastic section modulus of different sections:
1] Circular Section:
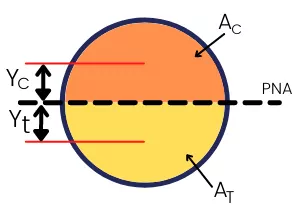
`Z_{p}` = `\frac{d^{3}}{6}`
How to get this…
For circular section, the plastic neutral axis passes through the center of circle that divides `A_{C}` and `A_{T}`.
The areas are given by,
`A_{C}`=`A_{T}`=`\frac{\pi d^{2}}{8}`
and `Y_{C}`=`Y_{t}`=`\frac{2d}{3\pi }`
`\sum A_{C}Y_{C}`=`\frac{\pi d^{2}}{8}\times (\frac{2d}{3\pi })`=`\frac{d^{3}}{12}`
`\sum A_{T}Y_{T}`=`\frac{\pi d^{2}}{8}\times (\frac{2d}{3\pi })`=`\frac{d^{3}}{12}`
The plastic section modulus for a circular section is given by,
`Z_{p}` = `\sum A_{C}Y_{C}` + `\sum A_{T}Y_{T}`
`Z_{p}` = `\frac{d^{3}}{12}` + `\frac{d^{3}}{12}`
`\mathbf{Z_{p} = \frac{d^{3}}{6}}`
2] Rectangle:
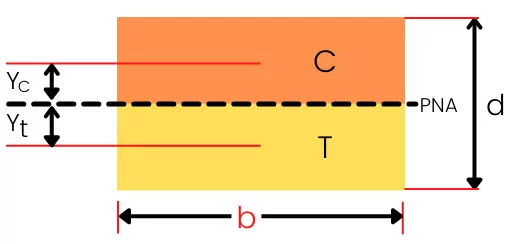
`Z_{P}` = `\frac{bd^{2}}{4}`
How to get this…
For the rectangular section, the plastic neutral axis passes through the center of height of cross-section.
Therefore,
`A_{c}` = `\frac{bd}{2}`
`A_{T}` = `\frac{bd}{2}`
and
`Y_{c}` = `Y_{t}` = `\frac{d}{4}`
Now, `\sum A_{C}Y_{C}` = `\frac{bd}{2} \times \frac{d}{4}` = `\frac{bd^{2}}{8}`
And, `\sum A_{T}Y_{T}` = `\frac{bd}{2} \times \frac{d}{4}` = `\frac{bd^{2}}{8}`
The plastic section modulus for the rectangular section is given by,
`Z_{P}` = `\sum A_{C}Y_{C}`+`\sum A_{T}Y_{T}`
`Z_{P}` = `\frac{bd^{2}}{8}`+`\frac{bd^{2}}{8}`
`\mathbf{Z_{P} = \frac{bd^{2}}{4}}`
Section modulus units
The unit for section modulus is the same for the plastic section modulus and for elastic section modulus.
The unit of section modulus is given by,
`Z_{e}` = `\frac{I}{Y_{max}}` = `\frac{m^{4}}{m}` = `m^{3}`
In the SI system, the unit of section modulus is m³. In the FPS system, the unit of section modulus is ft³.
Read also: