Contents:
What is isothermal compression?
Isothermal compression is the process of reducing the volume of a certain mass of fluid, by keeping its temperature constant throughout the process. In other words, it is a process of compression in which the system temperature remains constant throughout the process.
i.e. T = Constant
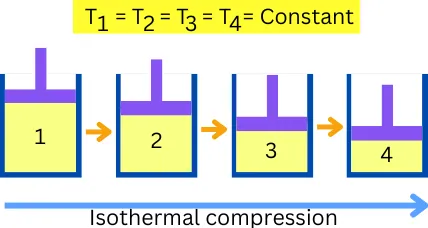
Isothermal compression is an ideal process that is used in a Carnot cycle.
During the compression, the work of compression is converted into heat. This heat can raise the temperature of the system. But in isothermal compression, the system has to reject the same amount of heat, to maintain a constant temperature (thermal equilibrium) throughout the process.
For the isothermal compression of the ideal gas, the temperature is constant, therefore the ideal gas equation becomes,
PV = mRT
As mRT = Constant,
∴ PV = constant
Is Isothermal compression possible?
The isothermal process is a quasi-static process which means that the process occurs slowly to remain the system in thermodynamics equilibrium.
But the compression process is a faster process, therefore during compression, the temperature of the system also increases.
Hence it is not possible to maintain a constant temperature during the compression process, therefore in actual conditions, isothermal compression is not possible.
Isothermal compression PV and TS diagram:-
The below figure shows the PV diagram and TS diagram for the isothermal compression process.
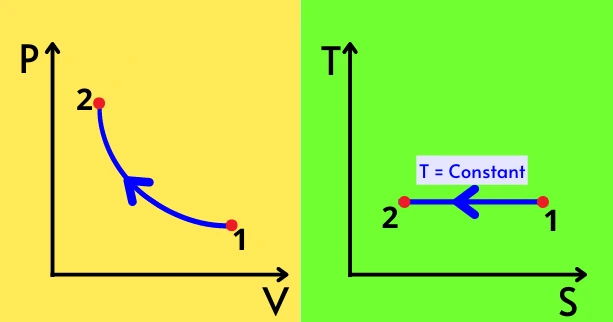
The PV graph shows the product of pressure (P) and volume (V) is constant over the isothermal compression process. The process on the TS diagram shows the temperature is constant throughout the process while the entropy of the system decreases.
Isothermal compression work:-
For the isothermal compression process, the formula for the work done is given by,
`W=mRT\times ln[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]`
As during compression, V2<V1, the work done becomes negative. Here -ve sign indicates that work is done on the fluid for the compression.
Derivation for work done:
For the isothermal process, the relation between P and V is given by,
P.V = P1.V1 = P2.V2 = Constant
∴ `P = \frac{P_{1}.V_{1}}{V}`
The work of the compression is given by,
`W = \intP.dV`
`W = \int_{V_{1}}^{V_{2}} \frac{P_{1}.V_{1}}{V}.dV`
`W = P_{1}.V_{1}\int_{V_{1}}^{V_{2}} \frac{1}{V}.dV`
`W = P_{1}.V_{1}[lnV]_{V_{1}}^{V_{2}}`
`W = P_{1}.V_{1}[lnV_{2}-lnV_{1}]`
`W = P_{1}.V_{1}.ln[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]`
As P1V1 = mRT1 = mRT
∴ `\mathbf{W = mRT.ln[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]}`
Isothermal compression formula/equation:-
Some of the formulae of the thermodynamic properties in the case of the isothermal compression process are as follows,
i] PV relation:
As PV = constant, the relation between pressure and volume for isothermal compression is given by,
P1V1 = P2V2
OR
`[\frac{P_{1}}{P_{2}}]=[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]`
ii] Change in internal energy:
As the value for ∆T is zero, therefore value for change in internal energy is also zero.
du = 0
iii] Heat transfer:
As per the first law of thermodynamics,
Q – W = ΔU
For an isothermal process, internal energy ΔU = 0.
∴ Q = W
Therefore the heat transfer in isothermal compression is given by,
`Q=mRT\times ln[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]`
As V2<V1, the Q becomes negative. Here the negative sign indicates heat is rejected by the system.
iv] Change in entropy:
The change in entropy during the isothermal process is given by,
`\Delta S =mR\times ln[\frac{V_{2}}{V_{1}}]`
v] Change in enthalpy:
The change in enthalpy for the isothermal compression process is zero.
∆h = 0
FAQs:
-
Is heat transfer takes place during isothermal compression?
The heat transfer during isothermal compression is necessary to remove the heat of compression to maintain thermal equilibrium.
-
What is the equation for the isothermal compression of an Ideal gas?
The isothermal compression of an ideal gas is represented by the following equation.
P.V = Constant
Read also: